- ✅ Introduction (Web2.3 – 2025)
- ✅ Chapter 2: Tools for Teaching and Learning
- ✅ Chapter 3: Tools for Communication
- 🗂 Microsoft Teams Communication & Collaboration & Video conferencing
- Chapter 3.4 Update Social media Sites – Pinterest, Instagram
- 🔁 update Pinterest
- 🔁 Update Instagram
- Chapter 3.5 Update Messenger Tools - WhatsApp
- 🔁 Update WhatsApp
- Chapter 3.6 update Screen Sharing Tools
- 🆕 AnyDesk (by AnyDesk Software GmbH)
- 🆕 FastViewer (by Matrix42 GmbH, Germany)
- Chapter 3.7 Update Video Sharing Tools – TikTok, YouTube
- 🔁 Update TikTok
- 🔁 Update YouTube
- Chapter 3.8 Update Social media - Facebook
- 🔁 Update Facebook
- ✅ Chapter 4: Tools for Collaboration
- 🆕 Metis (collaboration platform)
- 🔁 OneDrive Integration in Microsoft Teams for VET Education
- 🔁 OwnCloud
- 🎓 Moodle LMS Update
- 🔁 Ilias – Updated (2025)
- 🔁 Meistertask – Updated (2025)
- 📱 Miro (Online Whiteboard)
- 🆕 Obsidian (digital notebook for organizing knowledge)
- 🆕 Otter.ai (speech-to-text and meeting transcription tool)
- 🔁 Asana (update project and task management tools)
- ✅ Chapter 5: Tools for Creativity
- ✅ Chapter 6: AI Tools for VET
- 6.1 🆕 ChatGPT (by OpenAI)
- 6.2 🆕 Canva AI
- 6.3 🆕 Napkin AI (Visual AI for Vocational Education)
- 6.4 🆕 Microsoft Copilot (AI-powered assistant for vocational education)
- 6.5 🆕 Gemini (by Google)
- 6.6 🆕 Grok (AI model by AI for vocational education)
- 6.7 🆕 GrammarlyGO
- 6.8 🆕 JEDA.AI (Digital Board Tool)
- 6.9 🆕 Perplexity AI
- 6.10 🆕 VIDU.AI (AI Video Generator)
- 6.11 🆕 Nano Banana (AI creative content generator)
- 6.12 🆕 Deepseek (AI supporting VET)
- News of partner countries
Partners:
FA-Magdeburg | Germany
Rogepa | Romania
DiDi For a Better World | Türkiye
SBH Nordost | Germany
Lodz Chamber of Industry and Commerce| Poland
EPRALIMA Escola Profissional do Alto Lima CIPRL | Portugal
Lviv Polytechnic National University | Ukraine
✅ Introduction (Web2.3 – 2025) #
from IV4J to GPS4VET: Empowering VET with Web 2.3 and AI #
The core mission of the GPS4VET project (formerly IV4.euJ – Innovative VET for Jobs) is to demonstrate how Vocational Education and Training (VET) can benefit from modern Web 2.x tools and AI-powered learning environments. The project goes beyond simply highlighting digital tools—it provides concrete pedagogical integration strategies and good practice models for trainers, educators, and policymakers across Europe.
Digitalization in VET is not just a technical upgrade; it transforms the essence of teaching and learning. Our approach is grounded in the belief that VET must evolve toward ubiquitous, continuous, and lifelong learning—and that this transformation must remain accessible, inclusive, and meaningful.
We in the GPS4VET team believe that the implementation of Web 2.x tools does not disrupt the trainer-apprentice relationship. Even within constructivist and learner-centred paradigms, it remains possible to orchestrate active learning within structured workshops and training sessions. Web 2.x enables this orchestration with greater interactivity, creativity, and learner autonomy.
Moreover, the push toward digital transformation in VET is not just a matter of technology—it is driven by industry demands. The world of work requires apprentices who are:
- ✅ Immediately competent for today’s job roles, and
- 🚀 Prepared to innovate, adapt, and co-create within their sectors.
Whether in traditional fields such as automotive, agriculture, or health services, or in new economy branches like green tech or digital manufacturing, employees must show entrepreneurial thinking, creativity, and collaboration skills.
In this Guide we present real-life examples and tools showing that Web 2.x methods go beyond the traditional teach–train–test model. They support a culture of progressive learning, where young professionals are guided into reflective, autonomous, and future-oriented roles.
Lifelong learning in VET is no longer optional—it’s a strategic necessity. Workers are no longer just recipients of instructions; they are co-designers of processes, problem solvers, and change agents. With the right digital ecosystem, this development becomes possible and tangible.
We invite you to explore this guide with curiosity and courage. The tools and examples you’ll find here are not only usable—they are transformational.
Updated Chapters 1: Research all over Europe #
Germany
Germany has a dual VET system combining in-company training with part-time vocational school (Berufsschule). Digital tools are increasingly integrated into curricula, including LMS, collaboration platforms, and simulation-based learning. Green skills and AI literacy are emerging priorities supported by government initiatives like “DigiVET” and the “DigitalPakt Schule”.
Poland
Poland’s VET system offers school-based vocational programmes at secondary and post-secondary levels, often combined with internships. Reforms have improved employer cooperation and curriculum flexibility. Digitalization is advancing through national strategies, EU funding, and strong broadband infrastructure. Moodle, Google Workspace, and interactive e-learning platforms are increasingly used. Challenges remain in digital skills development, especially among teachers and rural learners.
Romania
Romania’s VET system includes technical high schools and post-secondary education. Recent reforms support digitalization, including investments in infrastructure and teacher training. EU-funded projects promote entrepreneurship and online learning tools, particularly in rural regions. Platforms like Moodle and Microsoft Teams are in growing use.
Spain
Spain offers VET through basic, intermediate, and advanced levels, with strong public-private cooperation. The country promotes blended learning, especially since COVID-19. Initiatives like “FP Digital” integrate digital skills into VET. Google Workspace and Moodle are widely used. Emphasis is placed on sustainable development and social inclusion.
Türkiye
Türkiye’s VET system is managed by the Ministry of National Education (MoNE). Since 2020, digital transformation programs have been accelerated, including content creation platforms and digital toolkits for teachers. EBA (Eğitim Bilişim Ağı) is the main digital learning portal. AI and green economy topics are being piloted in technical schools.
Ukraine
Ukraine’s VET reform is influenced by EU integration efforts. Despite challenges from the war, digital learning has expanded rapidly, supported by international donors. VET schools now use tools like Zoom, Google Classroom, and national platforms (e.g., Diia Education). Mobile learning, mental health support, and resilience-building are key themes.
Updated Chapters 2–5: Web 2.3 Tools for VET and New 6 AI #
✅ Chapter 2: Tools for Teaching and Learning #
Updated focus: Emphasizing flexible, blended, and AI-supported learning environments.
Introduction and Approach (Updated) #
In today’s VET landscape, digitalization is no longer optional—it’s essential. Learners expect interactive, flexible learning experiences, and educators need smart tools to design, deliver, and assess learning effectively.
Web 2.x tools provide this foundation by enabling learners to create, collaborate, communicate, and reflect. In the VET context, they bridge the gap between theory and practice, school and workplace, teacher and learner. With the rise of hybrid and AI-enhanced education, the integration of Web 2.x tools supports:
- 🎓 Competence-oriented learning: Tools help build both vocational and transversal competences (e.g., digital, social, entrepreneurial).
- 📱 Mobile and flexible access: Learners engage with content anytime, anywhere, on any device.
- 🌐 Real-world connection: Web tools allow interaction with professionals, employers, and international peers.
- ✍️ Personalized learning: Adaptive feedback and learner-created content foster ownership and motivation.
- 🤖 AI-enhanced support: New tools (e.g., ChatGPT, Canva Magic) help with feedback, content creation, and cognitive scaffolding.
Approach:
This guide classifies Web 2.x tools based on function, not brand. Each tool or platform is illustrated with a short description, usage model (free/paid/account), and VET-relevant example.
🔍 The Role of Web 2.x in Vocational Education and Training (VET)
Web 2.x tools empower learners and trainers in VET through participatory, interactive, and collaborative environments. Unlike traditional top-down instruction, these tools promote learner engagement, personalization, and practical skill development.
Key contributions of Web 2.3 in VET:
- ✅ Active Learning: Learners contribute content, participate in discussions, and collaborate on real-world tasks.
- 🌍 Authentic Communication: Platforms enable global dialogue, peer feedback, and networking with industry experts.
- 📱 Digital Competence: By using digital tools, learners acquire transversal digital skills valued in all sectors.
- 🧠 Self-directed Learning: Tools like blogs, wikis, and AI assistants support independent learning and reflection.
- 🤝 Workplace Simulation: Interactive environments simulate work tasks, supporting problem-solving and career readiness.
- 🌿 Sustainability & Inclusion: Web 2.0 tools help reach disadvantaged learners and promote eco-responsible practices.
In the context of VET, Web 2.x is more than a set of tools—it is a mindset of openness, participation, and adaptability.
Chapter 2.1 Tools and Platforms – Update (2025) #
Original Focus: Lists of tools and categories.
Update (Web2.3): Emphasis on hybrid learning, mobile compatibility, AI-enhanced tools.
2.1 Web 2.x Tools and Platforms – Updated Overview
The landscape of digital tools in VET is evolving. Web 2.x platforms now focus on inclusivity, collaboration, and increasingly, AI augmentation. Below are revised categories with tool examples:
|
Category |
Description |
Tools (2025) |
|---|---|---|
|
Communication & Video |
Real-time or asynchronous communication and exchange. |
Zoom, Microsoft Teams, Jitsi Meet |
|
LMS / Content Delivery |
Manage courses, assessments, and feedback. |
Moodle, Google Classroom, Canvas, LMS WordPress |
|
Collaboration |
Work together on shared documents, boards, or code. |
Miro, Padlet, Trello, GitHub, Meistertask |
|
Creativity & Publishing |
Design, present, or publish visual or written content. |
Canva, Adobe Express, Genially |
|
AI-powered Tools |
Content generation, feedback, automation, simulation. |
ChatGPT, GrammarlyGO, Canva Magic, Copilot |
|
Mobile & Microlearning |
Tools supporting on-the-go, bite-sized learning. |
Quizlet, Duolingo, Kahoot, TED-Ed |
|
Social Media & Blogs |
Reflection, visibility, outreach. |
Blogger, WordPress, Instagram (Edu accounts) |

🔁 Notion #
Link: https://www.notion.so/
Chapter context: Chapter 2 (Teaching & Learning), Chapter 3.1 (Communication), Chapter 5.4 (Project Management)
What it is
Notion is an all-in-one digital workspace that combines the functions of notes, documents, task management, databases, and collaboration tools. It allows users to organize, link, and visualize information in a flexible and structured way.
Users can create pages that contain text, images, videos, checklists, tables, or embedded content (like Google Docs, PDFs, or YouTube videos). Each page can be connected to others through links or databases, turning Notion into a powerful, customizable knowledge base.
Notion can function as:
- A project management tool (with Kanban boards, task lists, or timelines)
- A learning journal or portfolio
- A shared classroom workspace
- A resource hub or wiki
Why it is useful for VET
Notion supports project-based, competence-oriented, and self-directed learning—all essential for vocational education and training. It can be used to:
- Plan and document individual or group projects.
- Create digital portfolios where trainees reflect on their learning and showcase progress.
- Organize learning materials, schedules, and assignments in a single workspace.
- Facilitate collaboration and communication between students, teachers, and workplace mentors.
- Track competencies and link evidence of skills (photos, videos, reports, certifications). Its highly visual and structured design encourages learners to take ownership of their learning processes while helping educators monitor progress transparently.
How to
- Go to Notion.so and sign up with an email or Google account.
- Create or join a workspace (a shared digital environment for teams, classes, or projects).
- Add pages for projects, lessons, resources, or portfolios.
- Use templates such as “Project Tracker,” “Weekly Agenda,” “Learning Journal,” or “Portfolio” to get started quickly.
- Share pages with peers or teachers for feedback and collaboration.
Notion is available on the web, desktop (Windows/Mac), and mobile devices (iOS/Android). Changes sync automatically across devices.
Usage
💡 Free personal plan available (includes unlimited pages and blocks).
🎓 Education plan offers free upgrades for verified students and teachers.
🔑 Account required (sign in via Google or email).
🌐 Cross-platform access — use via browser or app on any device.
💠 Paid plans (Team and Enterprise) provide advanced permissions, analytics, and collaboration tools.
Learning Example
A team of vocational design students uses Notion to coordinate a client project. They:
- Plan tasks in a Kanban board (research → concept → prototype → delivery).
- Document their process with images, meeting notes, and uploaded drafts.
- Embed a cost-tracking table and a feedback log from their mentor.
- Use a shared portfolio template to present their outcomes during assessment week.
Their instructor monitors the workspace to give feedback on progress and teamwork, while students gain experience using a real-world productivity tool used by many creative and tech companies.
Links
- https://www.notion.so/
- https://www.notion.so/product/education
- https://www.notion.so/templates
- https://www.notion.so/help
✅ Chapter 3: Tools for Communication #
🗂 Microsoft Teams Communication & Collaboration & Video conferencing #
Link: https://www.microsoft.com/en/microsoft-teams/group-chat-software
Chapter context: Communication, Collaboration, Video conferencing
What it is
Microsoft Teams is a collaboration platform combining chat, video meetings, file storage, and integration with Microsoft 365. It exists in 2 versions:
Why is it useful for VET
Microsoft Teams offers a range of tools for engaging learners in vocational settings:
📁 Class Teams Spaces Create structured environments for specific courses with channels for lectures, homework, discussions, etc.
📌 Assignment Manager Design and distribute assignments, track submissions, and provide feedback—all directly in Teams.
🎥 Video Conferencing Tools Live lessons with screen sharing, breakout groups for teamwork, and recording options.
🗂 Shared Files and Collaboration Seamless co-authoring of documents, spreadsheets, and presentations in Microsoft 365 (Word, Excel, etc.).
💬 Persistent Chat & Reactions Encourage peer interaction through threaded conversations, emoji reactions, and mentions.
📊 Integrated Apps Tools like Forms (for quizzes), Whiteboard (for brainstorming), and third-party apps like Kahoot or Miro.
📅 Calendar & Scheduling Organize lessons with calendar invites linked to email and classroom announcements.
How to
Create a Microsoft account and access Teams through browser, app, or desktop client.
Learning Example
A VET class on tourism organizes a group project and uses Teams for meetings, file sharing, and final presentation or:
🎓 Learning Example: Using Microsoft Teams in Vocational Education
Course Context: Hospitality Management – Event Planning Module Scenario: A group of apprentices collaborates to design a concept for a sustainable community event.
🧑🏫 Trainer Setup
- Creates a Class Team for the course with channels for “Concept Development,” “Budgeting,” “Marketing,” and “Final Presentation.”
- Uploads templates and resources in the “Files” tab.
- Schedules weekly live sessions using Teams Calendar and records them for later viewing.
👩💻 Apprentice Tasks
- Use chat and video meetings to brainstorm ideas.
- Collaborate on Excel budgets and PowerPoint presentations directly in Teams.
- Submit their event proposals via the Assignments tab and receive feedback from the trainer.
- Reflect on their learning by posting a short video diary in the “Reflections” channel using Microsoft Stream.
🎯 Learning Outcome
Students gain experience in remote collaboration, digital presentation tools, and structured teamwork—core skills for modern hospitality roles.
Usage
✅ Free with limited features
💠 Full integration via paid Microsoft 365
Links
– https://www.microsoft.com/en/microsoft-teams/group-chat-software
🧩 Microsoft Teams: Personal vs Business Use
|
Feature |
Personal Version |
Business/Education Version |
|---|---|---|
|
Access & Identity |
Uses personal Microsoft account |
Linked to organization/school domain |
|
Collaboration Scope |
Family/friends |
Teams within institutions or companies |
|
App Integration |
Limited |
Full Microsoft 365 + third-party apps |
|
Meeting Features |
Basic video calls, chat |
Advanced scheduling, breakout rooms, recording |
|
Data Governance |
Personal storage only |
Organization-level compliance and controls |
Key Point for VET Trainers: The Business/Education version provides more structured tools for managing class teams, assignments, attendance, and collaborative learning. The Personal version is best for casual interaction and cannot be centrally administered.

Chapter 3.4 Update Social media Sites – Pinterest, Instagram #
🔁 update Pinterest #
Pinterest is a visual discovery engine and social media platform where users can find, save, and share ideas in the form of images and videos called “pins,” organized into collections called “boards”. It’s used for discovering inspiration, planning, and shopping for various interests like recipes, home decor, fashion etc.
Pinterest can be a valuable tool in VET, serving as a visual resource and organization platform for students and instructors. It can be used to gather and share information, organize study materials, and even facilitate online portfolios and peer feedback.
Why is it useful for VET
1. Resource Gathering and Organization:
- Virtual Bulletin Board: Pinterest allows users to create boards for specific topics or courses, allowing for the organized collection of relevant articles, images, videos, etc.
- Keyword Search: Pinterest acts as a visual search engine, enabling students to find information related to their vocational field by using relevant keywords.
- Visual Learning: The visual nature of Pinterest is particularly useful for vocational fields that rely on visual aids, e.g. culinary arts, design, or technical trades.
2. Study and Project Support:
- Study Tips and Templates: Pinterest offers different study tips, time management strategies, and organizational templates that can be beneficial for students.
- Digital Portfolios: Students can create individual Pinterest boards to showcase their best work, creating a dynamic digital portfolio that can be easily shared and updated.
- Peer Feedback: Pinterest’s commenting feature allows for constructive criticism and feedback on student work, fostering a collaborative learning environment.
3. Connecting Theory and Practice:
- Real-World Applications: Pinterest can be used to find examples of how vocational skills are applied in the real-world, bridging the gap between a classroom and a firm.
- Inspiration and Ideas: Students can explore Pinterest to discover innovative ideas, design concepts, and solutions relevant to their chosen field.
4. Professional Development and Networking:
- Sharing Best Practices: Vocational educators can use Pinterest to share successful teaching strategies, lesson plans, and course materials with colleagues.
- Community Building: Pinterest can facilitate connections between students, instructors, and professionals in the field, fostering a sense of community and collaboration.
Thus, by leveraging Pinterest’s visual and organizational features, vocational educators can enhance the learning experience, promote student engagement, and prepare students for successful careers.
Links

🔁 Update Instagram #
Instagram is a photo and short-form video sharing social networking service owned by Meta Platforms. It allows users to upload media that can be edited with filters, be organized by hashtags, and be associated with a location via geographical tagging. Instagram is increasingly used in VET for both promotional and educational purposes. It serves as a platform for communication, brand building, and sharing information about college achievements and activities. Furthermore, Instagram can be leveraged to connect with potential students and employers, showcase practical skills, and build communities around shared interests.
Why is it useful for VET
-
- Sharing Information: Instagram can be used to disseminate information about vocational programs, industry trends, and career pathways.
-
- Promoting Practical Skills: Colleges can showcase the practical skills students are developing through photos and videos of hands-on training and projects.
-
- Fostering Community: Instagram can facilitate the creation of online communities where students can connect, share experiences, and learn from each other.
-
- Supporting Learning: Some vocational teachers are exploring how to use Instagram to support their teaching practices, though this area is still relatively unexplored.
Promotion and Branding:
- Supporting Learning: Some vocational teachers are exploring how to use Instagram to support their teaching practices, though this area is still relatively unexplored.
-
- Reaching Target Audience: VET institutions use Instagram to connect with young adults who are active on social media, making it a valuable platform for recruitment.
-
- Showcasing College Life: Instagram allows colleges to share photos and videos of their facilities, student activities, and achievements, providing a glimpse into the college experience.
-
- Building Brand Image: By maintaining a professional and engaging presence, TVET colleges can enhance their reputation and become more attractive options for prospective students.
At the same time, there can be some challenges and considerations:
-
- Building Brand Image: By maintaining a professional and engaging presence, TVET colleges can enhance their reputation and become more attractive options for prospective students.
-
- Lack of Social Media Strategies: Many VET institutions lack a formal social media strategy, leading to inconsistent and sometimes unprofessional use of Instagram.
-
- Importance of Professionalism: Maintaining a professional online presence is crucial to avoid harming the college’s reputation.
-
- Need for Clear Objectives: Colleges need to define clear objectives for their Instagram presence and ensure that their posts align with these objectives.
Thus, Instagram offers significant potential for both promoting VET and enhancing the learning experience for students. By developing clear strategies and focusing on engaging content, VET institutions can leverage this platform to connect with their audience, showcase their strengths, and support student success.
Links
https://njvet.ep.liu.se/article/view/5039
https://sajim.co.za/index.php/SAJIM/article/view/1685

Chapter 3.5 Update Messenger Tools – WhatsApp #
🔁 Update WhatsApp #
WhatsApp is a social media, instant messaging (IM), and voice-over-IP (VoIP) service owned by technology conglomerate Meta.
It can be a valuable tool in vocational training by facilitating communication, sharing resources, and fostering collaboration among students and instructors. It can be used to deliver lessons, share learning materials, and provide support, ultimately enhancing the learning experience and improving student engagement.
Why is it useful for VET
1. Communication and Support:
-
- Instant Messaging: WhatsApp allows for immediate communication between students, instructors, and even external mentors, enabling quick questions, clarifications, and feedback.
-
-
- Group Chats: Facilitates group discussions, collaborative problem-solving, and peer support among students.
-
- Direct Messaging: Enables personalized communication and individual support, addressing specific student needs.
-
- Announcements and Reminders: Quickly disseminate important information, deadlines, and updates related to the training program.
2. Resource Sharing and Learning:
-
- Multimedia Content: Shares videos, audio recordings, images, and documents related to the vocational training, such as tutorials, demonstrations, and examples.
-
-
- External Links: Provides access to relevant online resources, articles, websites etc.
-
- File Sharing: Easily distribute assignments, project guidelines, presentations, and other documents.
-
- Audio/Video Messages: Delivers lessons, feedback, or instructions through voice or video messages, especially useful for practical skills training.
3. Fostering a Dynamic Learning Environment:
-
- Interactive Learning: Use WhatsApp to conduct polls, quizzes, and surveys to assess understanding and engage students.
-
-
- Informal Learning: Encourage informal learning and knowledge sharing through group discussions and interactions.
-
- Reduced Isolation: Connect students with peers and instructors, combating professional isolation, especially during the transition to the workforce.
4. Addressing Specific Needs:
-
- Personalized Learning Paths: Delivers tailored learning content and support based on individual student needs and progress.
-
-
- Accessibility: Reaches students in remote areas with limited access to traditional learning resources.
-
- Cost-Effective: A low-cost solution for communication and learning, particularly beneficial in resource-constrained settings.
5. Enhancing Employability:
-
- Skill Development: Delivers training on in-demand skills, boosting students’ employability.
-
-
- Job Placement Support: Facilitates communication with potential employers, provide resume and interview support, and connects students with job opportunities.
-
- At the same time, there can be some challenges and considerations:
-
- Digital Literacy: Students and instructors should have the necessary digital skills to effectively use WhatsApp.
-
- Privacy and Security: Measures to protect student data and ensure responsible use of the platform should be implemented.
-
- Appropriate Use: Clear guidelines for using WhatsApp for educational purposes and avoid excessive or inappropriate use have ot be established.
Thus, by carefully integrating WhatsApp into VET programs, educators can create a more engaging, accessible, and effective learning experience, contributing to the success of their students.
Links
https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/14/17/10510
https://online-journals.org/index.php/i-jac/article/view/11381
https://landbot.io/blog/whatsapp-education-use-cases
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9230031
https://www.scirp.org/journal/paperinformation?paperid=110199
Chapter 3.6 update Screen Sharing Tools #
🆕 AnyDesk (by AnyDesk Software GmbH)  #
#
Link: https://anydesk.com/
Chapter context: Useful in Chapter 3.1 (Communication), Chapter 4 (Remote Work & Support)
What it is
AnyDesk is a remote desktop application that allows users to access and control computers from anywhere via the internet. It provides secure, high-performance connections, enabling real-time collaboration, remote troubleshooting, and file transfer between devices. It runs on multiple platforms, including Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS.
Why it is useful for VET
In Vocational Education and Training (VET), AnyDesk is particularly useful for IT, engineering, and digital media learners. It allows learners and trainers to perform remote technical support, collaborate on practical tasks, and demonstrate software installations or troubleshooting steps without being physically present. Trainers can use it to remotely access student machines, guide through configuration tasks, or monitor progress in real-time.
How to
Go to the website and download the application for your operating system.
- Install AnyDesk on both local and remote devices.
- Start the app and note the AnyDesk Address displayed.
- Enter the remote computer’s address to request access.
- The remote user accepts the session, allowing shared control or view.
- You can transfer files, chat, and adjust session permissions.
Learning Example
A student in IT support needs to help a classmate configure network settings on their PC. Using AnyDesk, they connect remotely, take control of the desktop, and demonstrate each configuration step while explaining it through voice or chat. This setup replicates a real-world remote support environment used by professionals.
Usage


🆕 FastViewer (by Matrix42 GmbH, Germany)  #
#
What it is
FastViewer is a software tool for online communication, remote support, and screen sharing.
It is often used in companies, schools, and training centers to enable distance learning, online meetings, or technical support.
Main Features
- Screen Sharing
- The presenter can share their screen to show presentations, programs, or workflows in real time.
- Ideal for training sessions or lessons.
- Remote Control
- With permission, another participant can control the presenter’s or trainee’s computer.
- Useful for hands-on exercises or remote troubleshooting.
- Online Meetings & Webinars
- Supports multi-user video conferences with chat, audio, and video functions.
- File Transfer
- Secure and fast exchange of files between participants.
- Security & Data Protection
- Encrypted connections (SSL/TLS).
- No permanent installation required (can be run as a temporary file or via browser).
Why is it useful for VET
- Learning and Working from Anywhere
- Trainees can participate in lessons or training sessions regardless of their physical location (e.g., company, vocational school, or home office).
- Practical Demonstrations
- Trainers can demonstrate software applications, machine controls, or workflows live.
- Trainees can actively participate using remote control to complete exercises.
- Efficient Communication
- Quick support and communication between trainers and apprentices.
- Especially useful in IT or office-related training fields.
- Documentation and Review
- Sessions can be recorded, allowing for later review or use as learning documentation.
- Cost and Time Savings
- No travel costs or time required for training sessions.
- Lessons can be scheduled flexibly.
- Promotion of Digital Skills
- Trainees gain experience with modern communication and remote work tools — essential digital competencies for today’s workplace.
How to
Option 1: Using FastViewer without Installation (Quick Start)
FastViewer is often provided as a portable application, meaning you can run it directly without installing it.
- Get the FastViewer file
- Usually, your company, trainer, or IT department sends you a FastViewer executable file (e.g. FastViewer.exe) or a meeting link.
- Run the file
- Double-click the file.
- It will open directly — no installation needed.
- Enter session details
- You may be asked to enter a session ID or meeting code provided by your trainer or host.
- Enter it and click Connect / Join.
- Join the meeting or training session
- Once connected, you’ll see the trainer’s screen, and they may allow you to interact or share your screen too.
Advantage: Perfect for trainees — no admin rights required, and nothing is permanently installed on the computer.
🖥️ Option 2: Installing FastViewer on Your PC
If you use it frequently (e.g. for company training or technical support), you can install it.
- Download from the official website:
🔗 Go to: https://www.fastviewer.com - Choose the right product version
- Look for FastViewer Instant Meeting or FastViewer Remote (depending on what your company uses).
- Run the installer
- Double-click the downloaded file (e.g. FastViewer_Setup.exe).
- Follow the on-screen setup instructions.
- Launch FastViewer
- After installation, open the program and log in (if your organization provides a login).
- Enter the session ID to join or host meetings.
🔒 System Requirements
- Windows (most versions supported), macOS, or mobile (Android/iOS)
- Stable internet connection
- Microphone and webcam (optional for video meetings)
💡 Tip for Training Environments
If you’re using it in a school or company network, your IT administrator might need to:
- Allow FastViewer through the firewall,
- Configure proxy settings, or
- Distribute a pre-configured version to all trainees.
Usage
- A monthly subscription for what is called the “Secure Advisor” licence (including up to 100 remote-clients) is € 28.35 (net) per room/channel when billed annually. (de)
- The equivalent “server installation” subscription is about € 37.75 (net) per installation per month when billed annually. (de)
- For the “Instant Meeting” version (web-conferencing/online meetings) earlier lists showed: one-time purchase € 979 for 1 room, or € 38/month to rent 1 room (or € 26.60/month per room if buying 2 or more rooms) when billed annually. (de)
According to another source: a licence for 1 concurrent session per year is € 348 (plus VAT) in the marketplace listing. (Matrix42 Marketplace)
Learning Example
An IT trainer demonstrates how to configure a network using FastViewer:
- All trainees see the trainer’s screen in real time.
- Each trainee then takes turns using remote control to complete a task.
- The trainer observes, provides feedback, and corrects mistakes — all online.
Links
Download from App Store: FastViewer

Chapter 3.7 Update Video Sharing Tools – TikTok, YouTube #
🔁 Update TikTok #
TikTok, known in mainland China and Hong Kong as Douyin, is a social media and short-form online video platform owned by Chinese Internet company ByteDance. It hosts user-submitted videos, which may range in duration from 3 seconds to 60 minutes.
It can be a valuable tool in VET by offering a platform for creating and sharing short, engaging educational videos. This “TikTok-style learning” can enhance learning experiences through accessible, on-demand content that aligns with modern learners’ preferences for short, focused bursts of information.
Why is it useful for VET
-
- Increased engagement and motivation: Short, visually appealing videos can capture attention and make learning more enjoyable, especially for tasks like demonstrating procedures or providing quick tips.
-
-
- Improved knowledge retention: The concise nature of TikTok videos allows for focused learning and repeated viewing, aiding in knowledge retention and recall.
-
- Skill development: Videos can be used to showcase practical skills, creative processes, and even soft skills like communication and teamwork.
-
- Accessibility and flexibility: TikTok’s mobile-first design allows learners to access training materials anytime, anywhere, making it suitable for diverse learning environments and schedules.
-
- Cost-effectiveness: Creating TikTok videos can be relatively inexpensive compared to traditional training methods, especially for tasks like demonstrations or skill-based training.
-
- Peer learning and collaboration: TikTok can facilitate peer learning through challenges, collaborative projects, and shared learning experiences.
-
- Exposure to diverse perspectives: TikTok can expose learners to various approaches and techniques from different experts, expanding their knowledge base.
-
- Demonstrating procedures: Short videos can showcase step-by-step instructions for tasks like using equipment, performing a specific technique, or following safety protocols.
-
- Explaining concepts: TikTok can be used to break down complex ideas into easily digestible short videos, making them more accessible to learners.
-
- Showcasing best practices: Learners can create videos demonstrating best practices for a particular task, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
-
- Promoting creativity and innovation: TikTok can encourage learners to think creatively and develop innovative solutions to challenges.
-
- Building a learning community: TikTok can facilitate interaction and knowledge sharing among learners, creating a sense of community and support.
At the same time, there can be some challenges and considerations:
-
- Content credibility: It’s crucial to ensure the accuracy and reliability of information presented on TikTok.
-
-
- Maintaining focus and avoiding distractions: It’s important to ensure that TikTok is used effectively to support learning and avoid distractions.
-
- Copyright and intellectual property: It’s essential to be mindful of copyright and intellectual property rights when using TikTok for educational purposes.
-
- Accessibility for all learners: Not all learners may have equal access to technology or be comfortable using TikTok, so alternative methods should be available.
Thus, TikTok can be a valuable tool in VET when used with a clear pedagogical approach. By leveraging its interactive features, educators can create engaging learning experiences, enhance skill development, and prepare students for success in their chosen professions.
Links
https://journals.umcs.pl/en/article/view/16195
https://library.apsce.net/index.php/ICCE/article/view/4599
https://www.ijfmr.com/papers/2025/1/36857.pdf

🔁 Update YouTube #
YouTube is a social media and online video sharing platform owned by Google. It can be a valuable resource in VET by providing readily accessible, visual demonstrations and tutorials that enhance learning and skill development. Its flexibility allows learners to access content at their own pace and revisit materials as needed.
Why is it useful for VET:
-
- Demonstrations: Videos can be used to demonstrate specific tasks, procedures, and techniques in various vocational fields, such as plumbing, electrical work, or carpentry.
-
-
- Tutorials: Step-by-step tutorials can guide learners through complex processes, helping them develop practical skills.
-
- Case Studies: YouTube can host case studies and real-world examples of how vocational skills are applied in different contexts.
-
- Industry Insights: Videos featuring industry experts, company tours, and discussions about emerging trends can provide valuable insights into specific vocational fields.
-
- Learner-Generated Content: Encouraging learners to create their own YouTube videos can improve their understanding of the material and foster peer learning.
YouTube Benefits:
-
- Accessibility and Flexibility: YouTube videos are available 24/7, allowing learners to access content at their convenience and revisit materials as needed for better understanding.
-
-
- Visual Learning: Many vocational skills are best learned through visual demonstration. YouTube provides a platform for instructors to showcase practical techniques, step-by-step procedures, and real-world applications.
-
- Diverse Content: YouTube offers a wide range of videos covering various vocational fields, from skilled trades to technical professions and even business-related skills.
-
- Cost-Effectiveness: YouTube is a free platform, making it an affordable resource for both educators and learners.
-
- Engagement and Motivation: Visual demonstrations and the ability to pause, rewind, and rewatch videos can enhance learner engagement and motivation.
At the same time, there can be some challenges and considerations:
-
- Quality Control: It’s important to ensure that videos used in VET are accurate, reliable, and aligned with industry standards.
-
-
- Licensing and Copyright: Educators should be aware of YouTube’s licensing policies and ensure that they are using videos legally.
-
- Integration with Formal Training: YouTube should be used as a supplementary resource alongside formal vocational training programs, rather than a replacement for qualified instruction.
Thus, by leveraging the accessibility and visual nature of YouTube, educators can enhance VET programs and empower learners with the practical skills they need.
Links
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/video_pedagogy_for_vocational_education.pdf
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/.
https://www.etf.europa.eu/sites/default/files/2019-08/video_pedagogy_for_vocational_education.pdf
https://injurity.pusatpublikasi.id/index.php/inj/article/view/210
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13636820.2023.2180423
https://elearningindustry.com/8-tips-effectively-use-youtube-in-elearning
Chapter 3.8 Update Social media – Facebook #
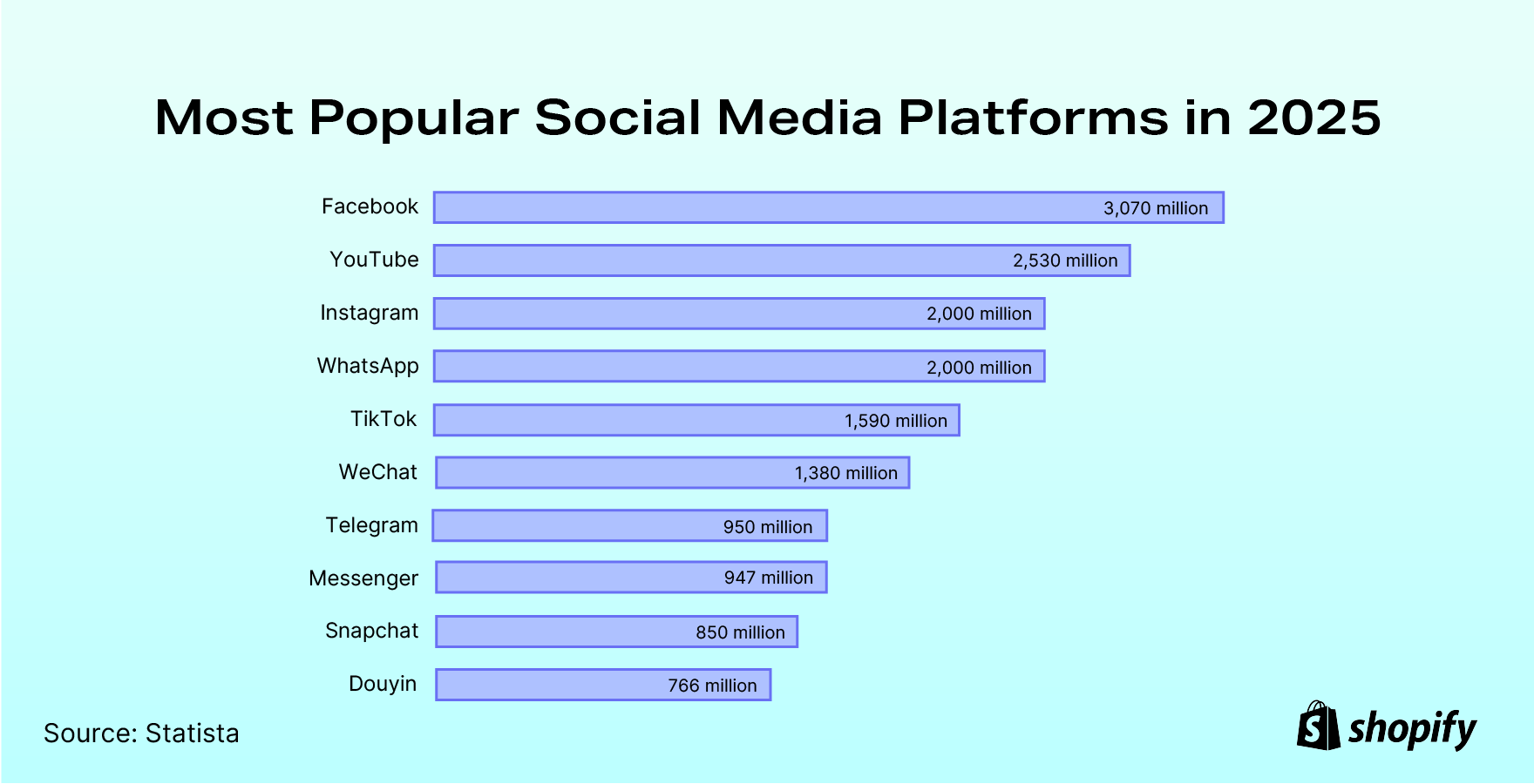
https://www.statista.com/topics/1164/social-networks
The leading social networks are usually available in multiple languages and enable users to connect with friends or people across geographical, political, or economic borders. In 2025, social networking sites are estimated to reach 5.42 billion users. Market leader Facebook was the first social network to surpass one billion registered accounts and currently has more than three billion monthly active users.
Social media can be a valuable tool in VET by enhancing learning, collaboration, and skill demonstration. It offers opportunities for students to access course information, collaborate on assignments, and showcase their acquired skills.

🔁 Update Facebook #
Facebook is a social media and social networking service owned by the American technology conglomerate Meta.
It can be a valuable tool in VET by facilitating communication, collaboration, and resource sharing among students and teachers. It can also help create a positive learning environment and enhance student engagement.
Why is it useful for VET
1. Enhanced Communication and Collaboration:
-
- Student-to-student and student-to-teacher interaction: Facebook allows for quick and easy communication between students and teachers, discussions, and collaborative learning.
-
-
- Resource sharing: Teachers can easily share learning materials, announcements, and updates with students, and students can share resources with each other.
-
- Building a learning community: Facebook can foster a sense of community among students, helping them feel more connected and supported in their learning journey.
-
- Connecting with industry professionals: Facebook can be used to connect students with professionals in their chosen fields, providing opportunities for networking and mentorship.
2. Increased Student Engagement:
-
- Reaching students where they are: Facebook is a platform that many students are already familiar with and use, making it an effective way to connect with them and encourage participation.
-
-
- Motivating learning: Facebook can be used as a motivational tool, with teachers sharing success stories, celebrating achievements, and providing positive reinforcement.
-
- Interactive learning experiences: Teachers can use Facebook to create interactive learning activities, such as polls, quizzes, and discussions, that can make learning more engaging and fun.
At the same time, there can be some challenges and considerations:
-
- Facebook addiction and academic performance: It’s important to be aware of the potential for Facebook addiction and its negative impact on academic performance.
-
-
- Privacy and data security: Schools and educators should be mindful of student privacy and data security when using Facebook for educational purposes.
-
- Digital divide: It’s important to ensure that all students have access to the technology and internet connection needed to participate in online learning activities.
-
- Teacher training and support: Teachers need adequate training and support to effectively integrate Facebook into their teaching practices.
Thus, by carefully considering these factors and implementing appropriate strategies, Facebook can be a valuable tool to enhance VET and empower students.
Links
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0280306
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6820203
https://ospi.k12.wa.us/sites/default/files/2023-08/facebookforeducators.pdf
https://online-journals.org/index.php/i-jet/article/view/9363
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/23311983.2023.2185447
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10639-021-10804-9
✅ Chapter 4: Tools for Collaboration #

🆕 Metis (collaboration platform) #
What it is
Metis is an open-source learning and collaboration platform developed in Germany, particularly tailored to support vocational training. It combines elements of a learning management system (LMS) with portfolio, project, and communication features.
Why is it useful for VET
Metis supports self-organized learning, work-based documentation, and collaborative project work—key elements in modern VET. Trainees can document their learning processes, share results, and receive feedback from teachers, trainers, and peers. It fosters both transparency and autonomy.
How to
Metis is hosted by regional education providers or schools. Learners receive login credentials and can access learning plans, upload work, and collaborate in digital learning spaces. Some institutions connect Metis with Moodle or Mahara.
Usage 

Learning Example
An apprentice documents their work-based learning in real time using a digital portfolio in Metis, linking it with media (images, PDFs, video reflections), while their mentor adds feedback asynchronously.
Links

🔁 OneDrive Integration in Microsoft Teams for VET Education #
What It Is: OneDrive is Microsoft’s cloud storage service. Within Teams, it acts as the personal file repository for each user and underpins file sharing, syncing, and collaborative editing.

-
- Each student and trainer get a personal cloud workspace.
-
-
- Documents shared in Teams channels or chats are stored in OneDrive or SharePoint.
-
- Enables seamless access to files across devices—ideal for hybrid or mobile learning environments.

-
- Upload & Share Learning Materials – Trainer’s store syllabi, worksheets, or reference docs in OneDrive and share links in Teams.
-
-
- Collaborative Workflows – Apprentices co-edit Word or Excel files saved on OneDrive in real time.
-
- File Version Control – Automatic backups allow students to restore earlier versions of assignments.
-
- Assignment Storage – Submitted tasks via Teams are stored and tracked through OneDrive-linked folders.

Course Context: Automotive Technology – Diagnostics Module Scenario: Apprentices complete a fault analysis task using shared documents and logbooks.

-
- Prepares an editable logbook template in Word, uploads it to OneDrive.
-
-
- Shares the link in the Teams “Diagnostics” channel for student access.
-
- Sets individual assignments for documentation and analysis.

-
- Each student downloads the logbook and enters their fault analysis.
-
-
- Saves their file in their personal OneDrive and shares it with the trainer.
-
- Uses Teams chat for clarification and feedback.
-
- Compares peer versions via a shared folder to learn different problem-solving approaches.

Learners gain skills in structured documentation, digital collaboration, and managing project artifacts using cloud tools—critical for modern technical professions.

-
- Seamless File Access: Students and trainers can reach their documents from any device.
-
-
- Collaboration: Real-time co-editing supports group projects and peer review.
-
- Version History: Keeps track of file changes so users can restore earlier work.
-
- Assignment Management: Stores files submitted through Teams assignments.

|
Function |
Use in Teaching |
|---|---|
|
Upload Learning Materials |
Trainers prepare resources and share via OneDrive links |
|
Group Work & Co-authoring |
Students co-edit worksheets or plans in real time |
|
Private Draft Storage |
Each learner saves individual drafts and reflections securely |
|
Peer Sharing |
Shared folders allow students to compare approaches and results |

Course Context: Automotive Technology – Diagnostics Module Scenario: Trainees document vehicle fault analysis using shared logbooks.
Trainer Actions:
-
- Uploads editable logbook template to OneDrive
-
-
- Shares the link in Teams under the “Diagnostics” channel
-
- Assigns task via Teams Assignments tab
Student Tasks:
-
- Completes logbook in Word and saves to personal OneDrive
-
-
- Shares finished file with trainer for review
-
- Discusses results via Teams chat and compares approaches in shared folder
Learning Outcome: Learners build documentation and cloud-based collaboration skills vital in modern technical roles.
Usage 

-
- Storage: 5 GB
-
-
- Cost: €0/month
-
- Includes: Basic file storage, sync across devices, access via web and mobile apps
-
- Ideal for: Light personal use, basic school tasks, mobile backups

|
Plan Name |
Monthly Cost |
Storage |
Extras |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Microsoft 365 Basic |
~€2/month |
100 GB |
Web versions of Word, Excel, Outlook |
|
Microsoft 365 Personal |
~€7–10/month |
1 TB |
Full Office apps + premium OneDrive features |
|
Microsoft 365 Family |
~€10–13/month |
6 TB (1 TB/user) |
Up to 6 users, ideal for households |

The participant can share their completed tasks with the trainer using the following link:






🔁 OwnCloud #
Link zur Quelle: https://owncloud.com
🔧 Why It’s Useful in VET
ownCloud belongs to the category File Sharing / Collaboration Tools. It enables secure storage, synchronization, and collaborative editing of files in a private cloud environment. Unlike public cloud services (e.g. Google Drive or Dropbox), ownCloud offers full data sovereignty by allowing institutions to run their own servers. It is a dedicated cloud system that can be deployed locally, thus meeting on-premise requirements and ensuring data storage within Germany. This makes it particularly suitable for schools, training centers, or public organizations with strict data protection requirements.
Usage model:
- Free: Community Edition (open source, requires own server)
- Paid: Enterprise Edition with professional support and advanced features
- Account: required, managed via own server or provider
Learning example:
In a vocational school project for construction and woodworking, students use ownCloud as a shared repository. They upload project reports, construction site photos, and CAD files. Teachers can assign tasks and provide feedback directly on the documents. Thanks to synchronization, all participants have access to the latest versions anytime, without relying on external cloud providers.
Learning videos:
Lehrvideos deutsch: 👉
- Wiki content https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/OwnCloud
- Owncloud 8: Erste Schritte
Beginner-friendly: Shows how to create users and groups, set up directories, and configure encryption. - Was ist ownCloud? ownCloud X erklärt! – neue Tutorialreihe
Basics explained: Provides an overview of the advantages of OwnCloud and shows how to set up dropzones – for teachers and administrators. - Owncloud und Qnap NAS Leichte App installation #Q14 …
For QNAP users: Step-by-step instructions for installation on a NAS – practical and easy to understand. - Tutorial: Raspberry Pi – OwnCloud installieren [GERMAN]
Tech-savvy? This video shows you how to install OwnCloud on a Raspberry Pi – ideal for DIY projects in education. - ownCloud auf FTP-Server oder Webspace installieren
For webspace users: Shows how to set up OwnCloud on a hosting package – including database connection and subdomain.

🎓 Moodle LMS Update #
Link: https://moodle.org/
Chapter context: Teaching & Learning
What it is
Moodle is a free, open-source learning management system (LMS) used to create personalized learning environments.
Why is it useful for VET
It allows trainers to organize courses, track progress, share content, and use quizzes. Suitable for blended and online training.
It features course management for creating, structuring and managing courses on various topics. User management allows roles such as trainer, participant, guest, etc. to be assigned. Learning activities can be divided into tasks, tests, forums, wikis, glossaries, surveys and interactive content, and linked together.
For evaluation purposes, assessments and feedback are possible in the form of grade books, rubrics, automatic assessments or individual feedback. Communication is managed via messages, forums, chat, calendars and announcements. The file management system allows the upload of various media formats, such as PDFs, videos, presentations, worksheets, etc.
The open source licence has resulted in numerous plugins and extensions with many additional modules and integrations (e.g. H5P, SCORM, Zoom, BigBlueButton).
The platform supports many languages, including German; barrier-free use is possible. With self-hosting, GDPR-compliant data protection standards can be maintained.
Moodle runs on a web browser but can also be used via apps (iOS, Android). It can be self-hosted or operated via a Moodle partner as a hosted solution (‘MoodleCloud’).
What’s new in 2025?
Moodle is evolving toward better usability, mobility, and flexible assessment workflows.
In vocational education, this means better structure, clearer communication, and targeted support — all digitally enhanced.
✅ 1. Improved Course Management & Navigation
|
Feature |
Benefit for VET |
|---|---|
|
Bulk Editing of course content |
Trainers/teachers can update or adjust multiple activities or course sections at once — helpful when adapting content for new apprenticeship cohorts. |
|
Redesigned Course Index |
Sections can be collapsed/expanded, helping apprentices navigate large or complex learning modules more easily. |
|
New Activity Cards |
Cleaner, more intuitive layout for assignments, quizzes, forums, etc. — especially useful for younger learners with limited Moodle experience. |
📝 2. Assessment & Feedback Enhancements
|
Feature |
Benefit |
|---|---|
|
Improved Gradebook |
Easier grading with filters and collapsible sections. Great for evaluating practical assignments, logbooks, or module tests. |
|
Inline Feedback Display |
Learners can instantly see their grade and the related feedback in one view — increases transparency and learning impact. |
|
Default Settings for Activity Completion |
Trainers can predefine activity completion rules — ideal for supporting self-paced learning or competency-based assessment. |
📱 3. Mobile Learning & Accessibility Improvements
|
Feature |
Benefit |
|---|---|
|
Moodle App 4.3+ Enhancements |
Better usability on smartphones/tablets — important as many apprentices use mobile devices for learning. Offline access, biometric login, and improved UI. |
|
Improved Visual Accessibility |
Color contrast, icons, and layout updates support inclusive learning — useful for learners with visual impairments or reading difficulties. |
|
Modern Course Page Design |
A fresher look makes online learning more engaging for digital-native trainees. |
💬 4. Better Communication & Motivation
|
Feature |
Benefit |
|---|---|
|
Notification Improvements |
Learners are informed when they are manually enrolled in courses — avoids confusion in group or module transitions. |
|
Improved Forums & Messaging (Web & App) |
Facilitates interaction and peer support — ideal for reflection, discussion, or collaborative learning in training projects. |
🏆 5. New Activities & Learning Features
|
Feature |
Benefit |
|---|---|
|
New “Ordering Question” Type |
Perfect for practice tasks where steps must be sorted in the correct order — e.g. procedures, workflows, accounting sequences. |
|
Advanced Reports / Report Builder |
Trainers can track progress and create custom reports — useful for mid-term assessments or performance reviews. |
|
Badge Enhancements |
Digital micro-credentials for completed modules or soft skills (e.g. “Excellent Communication”) — boosts learner motivation. |
🧩 Practical Use Cases in Vocational Training
-
- Usability: Use sorting questions for care procedures; document practical reflections as assignments with inline feedback.
-
- IT Training: Track project versions, provide structured feedback through the gradebook.
-
- Trades & Engineering: Use Book activity for safety topics; apply quizzes for retention checks.
-
- Business & Admin: Award badges for finished topics; use forums for case discussions; structured reporting for documentation.
How to
Visit moodle.org, set up a free account or use a hosted solution like MoodleCloud.
Learning Example
An instructor creates a digital course for apprentices in carpentry, integrating videos, assignments, and peer feedback.
Usage
✅ Free (self-hosted)
💠 MoodleCloud (freemium/paid options)
Links
- GPS WBL elias1-de vtt
![]() Introductory Video
Introductory Video
What it is
ILIAS is a powerful, open-source LMS originally developed at the University of Cologne. It provides tools for course creation, assessment, collaboration, and content structuring. The platform is SCORM-compliant and widely used in universities, public administration, and increasingly in VET.
The ILIAS learning system (Integrated Learning, Information and Work Cooperation System) is used at many universities, schools and companies. It supports digital teaching, learning and testing in vocational training and integrates various media and external tools.
🆕 What’s new in 2025
ILIAS has introduced improved mobile access, collaborative whiteboards, and AI-based assistance for trainers (e.g., quiz generation, feedback tools). The interface has become more user-friendly and accessible across devices.
Why is it useful for VET
ILIAS supports structured vocational courses with in-depth tracking and secure exam environments. New features allow blended and hybrid models, and institutions can customize the platform to suit industry-specific curricula.
Here are the main features of ILIAS:
🧩 It contains a Course management to create and organise courses and learning modules. Within these courses, participants and lecturers can be assigned different rights and viewing options. All courses can be structured using categories, folders and objects
📚 To provide learning content, it is possible to upload and provide files (PDFs, videos, presentations, etc.) and create or integrate interactive learning modules (SCORM, HTML, H5P). A glossary, literature lists and web links can be added.
📝 To evaluate the results, tests and examinations can be integrated via (multiple choice, gap-fill texts, free text, etc.), online examinations with automated evaluation, or there is the option of creating exercises with feedback.
📊 It includes learning progress monitoring with an overview of completed content, a feedback function for teachers (e.g. assessments, comments), and final surveys for course evaluation or opinion polling.
🧑🤝🧑 For effective communication and collaboration, ILIAS offers forums for discussions, chats within courses, the option to collaborate in closed group rooms, and course-related options for messages and notifications.
📆 In addition, calendars are available for planning course events and appointments, to-do lists and learning progress displays, and of course the option to register for or deregister from courses or events.
🔐 This includes dedicated user management, such as different roles and rights for administrators, tutors or participants, the option of self-registration or manual assignment, and integration of users with other systems (e.g. university administration, LDAP).
🔧 As an open platform, it can be customised with plugins and extensions, such as multilingualism and individual design, as well as the integration of external tools (e.g. BigBlueButton, Etherpad, Turnitin).
How to
Usually hosted by schools or regions. Learners and trainers log in via institutional access. ILIAS supports integration with other platforms like BigBlueButton or H5P.
To use the ILIAS learning system, you need a web host on which the platform can be installed and set up. Participants can access the ILIAS learning system from different devices via browser-based access.
https://docu.ilias.de/ilias.php?baseClass=illmpresentationgui&cmd=resume&ref_id=367
Various solutions are available in English and German, as well as templates optimised for schools and educational institutions with VET. Extensive documentation, FAQs and forums on the website provide support for getting started and for the ongoing maintenance and expansion of the portal.
https://docu.ilias.de/ilias.php?baseClass=ilrepositorygui&ref_id=3255
Usage
🆓 Open-source, account required.
🏫 Institutionally hosted; not typically available for individuals.
Learning Example
The Stiftung Bildung und Handwerk (SBH) uses ILIAS to offer a comprehensive blended learning curriculum for various vocational training and continuing education programmes. Learners access theory modules, upload practical reports and take part in video conference-based exams. Extensive tools for qualification and certification are available for employees and teachers. The following links provide a good overview of this.
- GPS WBL elias02-de vtt
![]() Introductory Video ILIAS / SBH, Germany
Introductory Video ILIAS / SBH, Germany

🔁 Meistertask – Updated (2025) #
What it is
MeisterTask is a cloud-based project and task management tool known for its simple interface and visual Kanban-style boards. It allows users to create and assign tasks, set due dates, add checklists, communicate through comments, and automate recurring workflows
🆕 What is new in 2025?
1. Subtasks
MeisterTask now supports subtasks, allowing for more granular task management. This feature is particularly useful for breaking down complex assignments into smaller, manageable steps, enhancing clarity and tracking.
2. Project Templates
The introduction of project templates enables educators and trainers to quickly set up standardized workflows for recurring projects, such as internships or training modules. This consistency aids in streamlining processes and saving preparation time.
3. MeisterNote Integration
MeisterNote has been integrated into MeisterTask, allowing users to create, manage, and link notes directly within tasks and projects. This integration facilitates seamless documentation and collaboration, making it easier to maintain comprehensive records of training activities.
4. Content Manager Role Restrictions
As of October 25, 2023, external users (those not part of the owning team) can no longer hold the Content Manager role in projects. This change enhances data security by ensuring that only authorized team members have full editing rights.
5. Changes to External Sharing
Starting December 7, 2023, users on the Basic (free) plan can no longer share projects or notes with external users. This policy aims to protect sensitive information and requires teams to upgrade to a Pro or Business plan for external collaboration features.
6. Mobile App Enhancements
The mobile applications for iOS and Android have received updates, including a redesigned home screen and improved navigation. These enhancements provide users with better access to tasks, checklists, and notifications on the go, supporting mobile learning and remote collaboration.
7. Live Pages
MeisterTask introduced Live Pages, allowing users to publish notes and share them via a link. This feature is beneficial for sharing training materials, guidelines, or project summaries with external stakeholders or learners
8. List View for Projects
A new List View option has been added to projects, providing an alternative to the traditional board view. This feature caters to different project management styles and can be particularly useful for users who prefer a linear task list.
9. AI Writing Assistant
The introduction of the AI Writing Assistant helps users improve their writing within notes by offering suggestions for summarization, content expansion, and paragraph generation. This tool can assist learners in drafting and refining reports or assignments. (support.meistertask.com)
Why is it useful for VET
In vocational schools and training programs, MeisterTask can serve as a digital tool for project-based learning, teamwork, and organizational skill development. It helps learners experience modern workplace collaboration in a structured, transparent environment.
Main benefits:
-
- Supports project-based learning: Learners plan, organize, and manage tasks like in real workplace projects.
-
- Team collaboration: Each task can be assigned to a responsible trainee, encouraging accountability and teamwork.
-
- Communication & feedback: Trainees and instructors can comment directly within tasks, attach documents, and track progress transparently.
-
- Self-management & time planning: Trainees practice prioritizing, meeting deadlines, and monitoring progress.
-
- Transparency & supervision: Instructors can track progress in real time, identify issues early, and provide targeted feedback.
How to
Here are steps and tips on how to incorporate MeisterTask into a training context:
-
- Create a project: Create a new project (e.g., ‘Final Project,’ ‘Customer Service Module’) and set up boards (Kanban) with columns such as To Do, In Progress, Review, Done.
-
- Define and assign tasks: Create tasks, checklists, due dates, and assign them to trainees or groups.
-
- Communication & feedback: Use comments within tasks to provide feedback or clarify questions.
-
- Automation & recurring tasks: Use automations for recurring tasks (e.g., weekly reports, feedback loops) according to your schedule.
-
- Clarify roles & rights: Determine who can edit tasks and who has view access to maintain clarity.
-
- Overview & reporting: Use timelines, reports, etc. to visualise progress (for learners & trainers).
-
- Integration & mobility: With apps available, trainees can also work on the go and view/edit tasks while travelling.
Her a short setup guide for an example project as pdf: MeisterTask_Vocational_Training_Guide
MeisterTask_Vocational_Training Introduction”
Learning Example
At Europaschule Utbremen (Germany), using MeisterTask reduced project-related administrative work by around 70%. (Source: MeisterTask Customer Stories
Usage
MeisterTask is available as a web app, desktop app, and mobile apps (iOS and Android). Register for an account and start collaborating using templates and drag-and-drop tools. The basic account is free. For Pro and Business account you have to pay ≈ 13 / 25 $ per months.
Links
📱 Miro (Online Whiteboard) #
Chapter context: Collaboration, Brainstorming, Project planning
What it is
Miro is an online collaborative whiteboard platform that allows teams to brainstorm, plan, and work visually. It is a web-based application that enables real-time visual collaboration, whether in the office or remotely.
What is new in 2025?
The new versions have integrated AI-powered tools that can verify and summarise questions and problems, as well as offer helpful support in text creation and feedback summarisation, such as Summarise Comment Threads / Conversation Summaries. Furthermore, there are now synchronised copies across multiple boards, in which changes are automatically applied. In the Templates/Miroverse area, there are numerous new templates, such as intelligent templates, community-driven templates and templates specifically for agile methods.
There is a new design that includes a global colour picker, modernised sticky notes, redesigned icons, updated reactions and stickers. Integrations with tools such as Azure DevOps, GitHub, Salesforce, Autodesk and others, often with bidirectional sync, are now also possible.
Why is it useful for VET
The use of Miro in vocational training can bring a variety of educational and practical benefits. Especially in the context of modern, digitally supported training, Miro offers many opportunities to improve learning processes and promote collaboration as a visual and collaborative platform. Trainees can visually organise ideas, workflows or projects. Trainers can use it for group planning and online workshops.
Advantages of Miro in vocational training
1. 🧠 Promotion of active and visual learning
-
-
- Learning content can be presented visually (e.g. mind maps, flowcharts, timelines).
-
- Promotes creative thinking and better understanding through the visualisation of complex relationships.
-
2. 👥 Teamwork & collaboration
-
-
- Trainees can work on a board at the same time – ideal for group work or project work.
-
- Supports the development of social skills and teamwork.
-
- Feedback and ideas can be contributed directly via comments or live collaboration.
-
3. 🌍 Location-independent and flexible learning
-
-
- Ideal for hybrid or digital training formats.
-
- Trainees and trainers can access content anytime, anywhere.
-
4. 🔄 Interactive learning methods
-
-
- Integration of interactive exercises, e.g. drag-and-drop tasks, assignments or virtual brainstorming.
-
- Supports methods such as design thinking, learning circles or business games.
-
5. 📚 Structuring and organising learning processes
-
-
- Visualisation of learning plans, project progress or work assignments.
-
- Progress can be documented and regularly reviewed (e.g. with Kanban boards).
-
6. 🧩 Integration with other tools
-
-
- Integration of content from tools such as Microsoft Teams, Google Drive, Trello or Slack.
-
- Facilitates organisation and saves time.
-
7. 🎓 Promote independent learning
-
-
- Trainees can create their own boards, e.g. for exam preparation.
-
- Promotes personal responsibility, self-organisation and digital know-how.
-
How to
Register for a free account and start collaborating using templates and drag-and-drop tools.
Learning Example
During a vocational workshop, students in a logistics class map out a delivery process flow using Miro.
Usage
✅ Free plan for small teams
💠 Premium features via paid subscription
Links
 #
#
🆕 Obsidian (digital notebook for organizing knowledge) #
What is it?
Obsidian is a digital notebook that helps you collect, organize, and connect notes in one place. It works like a personal workspace where you can keep all your ideas, materials, and documents together.
Why is it useful for VET
In VET, Obsidian can be used by teachers and learners to record project work, reflections, and progress. It helps to link related topics, store materials, and see how different parts of learning connect. It’s useful for teamwork, self-study, and documenting results.
How to
You can download Obsidian for free on your computer or phone. Create folders for subjects or projects, add notes, and use links or tags to connect information. It can also work together with cloud services to share materials with others.
Usage
Free for personal and educational use.
Works offline.
No account needed – all data stays on your device.
Learning Example
Students use Obsidian to collect ideas, notes, and pictures from their practical training. They connect notes about skills, tools, and feedback, creating a clear overview of what they have learned.
🆕 Otter.ai (speech-to-text and meeting transcription tool) #
What is it?
Otter.ai is a tool that automatically turns spoken words into written text. It can record meetings, lessons, or interviews and create accurate transcriptions that are easy to read and share.
Why is it useful for VET
In VET, Otter helps teachers and students keep written records of discussions, online classes, or project meetings. It supports accessibility, note-taking, and understanding for learners who prefer reading or reviewing materials later.
How to
You can use Otter on the web or as a mobile app. Start recording or upload an audio file, and the tool will generate a text version automatically. You can edit, highlight, and share the transcript with others.
Usage
🆓 Free plan available with limited minutes.
💻 Works on web and mobile.
🔑 Account required.
Learning Example
A VET teacher records a workshop on green technologies using Otter.ai. After the class, students receive the transcript to review key points and vocabulary.
Links
• https://otter.ai
• https://help.otter.ai
🔁 Asana (update project and task management tools) #
What is it?
Asana is an online tool that helps teams plan and organize their work. It allows users to create
projects, assign tasks, set deadlines, and track progress in one clear workspace.
Why is it useful for VET
In VET, Asana can help teachers, trainers, and learners manage group projects, training tasks, or
events. It supports teamwork, responsibility, and time management—skills that are essential in
vocational education.
How to
You can sign up for a free account and start by creating a new project. Add tasks, assign them to
team members, and set due dates. The visual boards and timelines make it easy to see what
needs to be done and when.
Usage
Free basic version available.
Works in browser and as a mobile app.
Account required to collaborate with others.
Learning Example
A VET class uses Asana to plan a local sustainability fair. Each student group manages different
tasks—such as promotion, logistics, and presentations—while the teacher monitors progress
and deadlines.
Links
• https://asana.com
• https://asana.com/guide
✅ Chapter 5: Tools for Creativity #
Adobe Express (Design platform) #
Link: https://express.adobe.com/
Chapter context: Creativity, Presentation, Design
What it is
Adobe Express is a simplified design platform that lets users create social graphics, flyers, logos, and short videos.
Why is it useful for VET
Vocational students in fields like marketing or hospitality can create brochures, menus, and presentations easily.
How to
Register for a free Adobe account and access templates and design tools.
Learning Example
A student designs a flyer for a bakery promotion using brand colors, AI templates, and royalty-free media.
Usage
✅ Free with account
💠 Premium assets and features via paid Adobe subscription
Links

🔁 Prezi (updated) #
Link: https://prezi.com/
Chapter context: Chapter 5.2 (Presentation tools), Chapter 3.1 (Communication)
What it is
Prezi is an interactive, cloud-based presentation platform designed to create visually engaging and story-driven presentations. Instead of traditional slides, Prezi uses a zoomable canvas that allows users to navigate between topics, subtopics, and details in a dynamic, non-linear way. This approach encourages more natural storytelling and helps audiences see the “big picture” alongside specific details.
Prezi offers three main tools:
-
- Prezi Present – for interactive, zoomable presentations.
-
- Prezi Video – integrates visuals and slides into live or recorded video presentations.
-
- Prezi Design – for creating infographics, reports, and data visualizations.
Why it is useful for VET
Prezi supports communication, creativity, and digital literacy—core competences in modern VET. It helps students and trainers:
-
- Present projects, portfolios, and case studies in visually compelling formats.
-
- Explain technical or process-oriented topics using visual hierarchies and zoom navigation.
-
- Enhance online learning and blended teaching, especially with Prezi Video for virtual presentations.
-
- Develop presentation and communication skills, which are valuable in all vocational fields. Its design flexibility also fosters visual thinking—helping learners understand and explain workflows, systems, or project phases more effectively.
How to
Visit Prezi.com and create a free account. Users can start from templates, import existing PowerPoint slides, or design from scratch. Presentations are stored in the cloud, enabling easy access and collaboration.
The Prezi Video tool allows presenters to appear next to their visual content during live sessions or recordings—ideal for remote or hybrid classrooms. The Prezi Design module enables users to create interactive charts, infographics, and reports for project documentation.
Learning Example
A hospitality student creates a Prezi presentation to illustrate customer service workflows in a hotel. The presentation zooms from an overview of departments to individual roles, showing how tasks connect in real time. During their final assessment, the student uses Prezi Video to present the workflow online, with their narration and visuals displayed simultaneously.
Usage
✅ Free basic plan (includes online editing and cloud storage)
💠 Premium plans available for additional features (offline access, advanced analytics, brand customization, and more)
Links
🔁 Google Slides (presentation platform updated) #
Chapter context: Chapter 5.2 (Presentation tools) Chapter 3.1 (Communication)
What it is
Google Slides is a free, web-based presentation platform that allows users to create, edit, and share slide decks online. As part of Google Workspace, it integrates seamlessly with other tools such as Google Drive, Docs, Sheets, and Meet. Users can design slides with text, images, videos, charts, and animations, and collaborate with others in real time. Presentations are automatically saved in the cloud, ensuring accessibility from any device with an internet connection.
Why it is useful for VET
In vocational education and training, Google Slides supports collaborative, project-based, and digital learning. It allows students and trainers to:
- ◦ Co-create and share presentations, reports, and portfolios in real time.
- ◦ Deliver interactive lessons and project showcases using multimedia elements.
- ◦ Practice team collaboration and digital communication — key 21st-century skills.
◦ Provide and receive feedback directly within shared presentations. Its integration with Google Drive and Google Classroom also makes it ideal for blended and distance learning setups common in modern VET programs.
How to
Go to Google Slides using a Google account (free to create). Users can start from a blank presentation or choose from ready-made templates. Slides are stored in Google Drive, allowing real-time editing, commenting, and sharing with others via link or email. Presentations can be delivered directly in the browser, embedded in other platforms, or downloaded as PowerPoint or PDF files.
Learning Example
A group of business administration trainees uses Google Slides to prepare a marketing pitch for a sustainable product. Each team member contributes content to the same slide deck simultaneously—adding visuals, graphs, and notes. Their instructor reviews the presentation online, adding comments and suggestions before the final live pitch session.
Usage


Links
🆕 Mentimeter #
What it is
Mentimeter is an online presentation and polling tool that allows teachers and trainers to create interactive quizzes, surveys, and word clouds in real time. Learners can participate easily by using their smartphones or laptops, entering a code to join the session. This increases engagement, motivates learners, and provides immediate feedback.
Why is it useful for VET
Mentimeter fits into the category of interactive presentation and collaboration tools (similar to tools like Kahoot or Padlet). It supports participatory learning approaches and can be used in both classroom and online environments.
How to
The general workflow:
a. Presentation Creation (Frontend + Backend)
-
The presenter uses the Mentimeter web app to design slides.
-
These slides and configurations are saved in the cloud (Mentimeter’s servers, likely using a backend like Node.js or similar).
-
The presentation is stored as structured data (JSON-like format) describing the slides, question types, and options.
b. Live Session
-
When the presenter starts the presentation, Mentimeter generates a session ID or code.
-
This code maps to a unique presentation session in the backend database.
c. Audience Interaction
-
Participants go to menti.com
Usage
Free version available (limited number of questions per presentation).
- Account required for creating presentations.
- Paid plans available for extended features (unlimited questions, advanced reporting).
Learning Example
In a vocational training class, the teacher introduces a new topic (e.g., safety regulations). Instead of a traditional lecture, learners are invited to answer live quiz questions via Mentimeter. The results are shown instantly on the screen, creating a collaborative discussion and allowing the teacher to identify areas where further explanation is needed.
Links
✅ Chapter 6: AI Tools for VET #
6.1 🆕 ChatGPT (by OpenAI) #
Link: https://chat.openai.com/
Chapter context: Useful in Chapter 2 (Teaching & Learning), Chapter 3.1 (Communication)
What it is
ChatGPT is an AI-powered assistant developed by OpenAI that generates human-like text responses. It can answer questions, explain concepts, summarize texts, support creative writing, or analyze documents and images. The current version, GPT-5 (2025), provides enhanced accuracy, longer memory, and multimodal capabilities (text + image input).
Why is it useful for VET
Vocational learners can use ChatGPT to understand technical concepts, prepare for exams, or get structured help with projects. Trainers can create learning materials, generate feedback, or design exercises. With GPT-5, ChatGPT is now able to handle more complex scenarios—for example, analyzing a project report together with a technical diagram or supporting collaborative assignments that require contextual accuracy.
How to
Go to the website and create a free account.
-
- GPT-3.5 is available for free.
-
- GPT-4 and GPT-5 are available in the Plus subscription (~$20/month), offering greater reliability, multimodal features, and advanced reasoning.
Learning Example
An apprentice in electronics asks: “What’s the difference between a transistor and a thyristor?” ChatGPT provides a detailed yet accessible explanation—and with GPT-5, it can also interpret a simple circuit diagram uploaded by the student, offering step-by-step clarification.
Usage
✅ Free with account GPT-3.5
💠 GPT-4 and GPT-5 via Plus subscription (~$20/month)
Links
– https://openai.com/chatgpt
– https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=chatgpt+in+education
6.2 🆕 Canva AI #
Link: https://www.canva.com/features/ai/
Chapter context: Chapter 5.12 (Image creation/editing), Chapter 5.2 (Presentation tools)
What it is
Canva AI offers creative automation tools like AI text-to-image, AI video assistant, magic writing, and smart design suggestions.
Why is it useful for VET
Students in design, business, or marketing vocations can use Canva to create professional materials. It’s also helpful for documenting projects or creating engaging presentations.
How to
Create a free account and start designing. Many AI tools are included in the free plan; advanced features require a Pro subscription.
Learning Example
A business apprentice creates an AI-generated flyer promoting sustainable fashion, using AI-generated images and layout suggestions.
Usage
✅ Free with account
💠 Pro features available (optional subscription)
Links
– https://www.canva.com/features/ai/
– https://www.canva.com/designschool/
6.3 🆕 Napkin AI (Visual AI for Vocational Education) #
What it is
Napkin AI is an AI-powered visualization platform that turns written text into editable visuals. It’s designed to simplify communication, enhance presentations, and support creative thinking. Users simply input their text, and Napkin generates relevant visuals such as:
- Flowcharts
- Mind maps
- Infographics
- Data charts
- Concept diagrams
All visuals are customizable and exportable in formats like .ppt, .pdf, .png, or .svg, making it easy to integrate into lessons, reports, or presentations.
Why it is useful for VET
Napkin AI supports hands-on, visual, and project-based learning in vocational education:
🎓 Visual thinking: Learners can structure and present ideas visually—ideal for planning, analysis, and documentation.
🧠 Simplifying complexity: Technical or theoretical content becomes easier to understand through diagrams and charts.
📊 Presentation skills: Napkin helps learners create professional visuals for assessments or client-facing projects.
🤝 Collaboration & communication: Teams can co-create visuals and use them to explain processes or findings clearly.
🌍 Cross-sector application: Useful in fields like logistics, healthcare, IT, business, and engineering.
How to use it
- Visit napkin.ai
- No prompting required—just paste your text
- Choose from auto-generated visuals and customize them
- Export in multiple formats for use in documents or slides
- Free starter access available; premium features offered during beta phase
Learning Example
🛠 Scenario: A VET class in logistics creates a process diagram for warehouse intake.
Trainer:
- Assigns: “Visualize the steps involved in receiving goods at a mid-sized company.”
Learners:
- Write a short description of the process
- Use Napkin to generate a flowchart
- Customize icons, colors, and labels
- Export the visual and present it in class
🎯 Outcome:
Learners gain a deeper understanding of the process, improve visual communication skills, and experience how AI can support clarity and creativity in vocational contexts.
Usage
✅ Free starter access
💠 Premium access available during beta
🔐 Data privacy governed by Napkin’s platform policies
🌐 Web-based, no installation required
Links
- https://www.napkin.ai
- Napkin AI for educators and professionals enablinglearning.com
- Napkin AI overview and examples Unterrichten Digital
Videos
DE: Dieses deutschsprachige Video von Unterrichten.Digital zeigt, wie du mit Napkin.ai aus einfachen Texten automatisch Diagramme und Infografiken erzeugst – perfekt für den Einsatz im Unterricht. Grafiken automatisiert aus Text erstellen (Vorstellung und Tutorial)
EN: Get PROFESSIONAL Visuals in Minutes NOT Hours with …
EN: Getting Started with Napkin.AI – Quick Examples
EN: Introduction Link
6.4 🆕 Microsoft Copilot (AI-powered assistant for vocational education) #

What it is
Microsoft Copilot is an AI-powered digital assistant designed to support learners, educators, and professionals in vocational education and training (VET). It uses advanced language processing to help with writing, research, ideation, organization, and communication. Copilot is integrated into Microsoft 365 apps (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Outlook) and also available as a standalone app across platforms.
Copilot can:
- Generate, revise, and summarize text
- Assist with presentations and spreadsheets
- Research and explain complex topics
- Personalize learning content
- Structure projects and visualize ideas
- Engage in interactive conversations and reflection
It adapts to the user’s context—whether in the classroom, workplace, or during self-directed learning.
Why it is useful for VET
Copilot enhances self-directed, competence-based, and creative learning. In vocational education, it can be used to:
🧠 Support learning: Copilot explains concepts, simplifies content, and generates quizzes for review.
📝 Assist writing: Learners can draft reports, applications, project descriptions, or reflections with Copilot’s help.
📊 Improve data literacy: In Excel, Copilot helps analyse data, create charts, and automate calculations.
🎓 Enable personalization: Copilot adjusts to the learner’s level, background, and goals.
🧩 Facilitate project work: Copilot helps structure ideas, document progress, and manage tasks—ideal for hands-on learning.
🌍 Support multilingual environments: Copilot understands and communicates in many languages, useful in diverse classrooms or for integration support.
How to use it
- Available within Microsoft 365 apps (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Outlook)
- Also accessible via standalone app (Web, Windows, iOS, Android)
- Sign in with Microsoft, Google, or Apple account
- Included in Microsoft 365 Education plans
- Compliant with EU data protection standards (see Microsoft Privacy Statement)
Learning Example
🛠 Scenario: A VET class in mechatronics creates a digital maintenance manual for a machine.
Trainer:
- Assigns the task: “Create a manual with descriptions, safety instructions, and maintenance schedule.”
- Shares a Word template via Microsoft Teams.
Learners:
- Use Copilot in Word to write technical descriptions
- Generate simplified safety instructions
- Build a structured outline and table of contents
- Use Copilot in PowerPoint to prepare a final presentation
🎯 Outcome:
Learners produce a professional document, practice technical writing, reflect on their work, and experience how AI can support learning and productivity—key skills for the future workplace.
Usage
✅ Included in Microsoft 365 Education
💠 Also available as a standalone app
🔐 GDPR-compliant for institutional use
🌐 Cross-platform access (Web, Desktop, Mobile)
Links
- https://copilot.microsoft.com
- https://learn.microsoft.com/copilot
- https://privacy.microsoft.com/privacystatement
🌍 English Tutorial Videos and other language
- Microsoft Copilot Tutorial Step-by-step guide to using Copilot in Windows and Microsoft 365 apps like Word, Excel, and PowerPoint.
- Microsoft Copilot Full Course For Beginners [2025] A complete beginner-friendly course covering prompts, tips, licensing, and use cases.
- Microsoft 365 Copilot Tutorial – Beginner’s Guide (2025) End-to-end walkthrough of Copilot’s features and how to use them effectively.
- Microsoft Copilot: The Ultimate Tutorial Covers real examples of Copilot in Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and debunks common myths.
- Microsoft Copilot Tutorial – A Beginner’s Introduction to Copilot Explains the difference between Copilot and ChatGPT, integration in 365 apps, and prompt strategies.
- Copilot Studio: Complete Tutorial for Beginners & For advanced users: shows how to build your own Copilot with Microsoft Copilot Studio.
- Get Started with Microsoft Copilot (Beginners Guide) Quick-start guide including image generation, song creation, and PDF analysis.
6.5 🆕 Gemini (by Google) #
![]()
Link: (Current Gemini Platform, e.g., accessible via Google services)
Chapter context: Useful in Chapter 2 (Teaching & Learning), Chapter 3.1 (Communication), Chapter 5.8 (Information & Research Tools) [based on similar tools in Chapter 6.
What it is
Gemini is an advanced Large Language Model (LLM) developed by Google. It is trained to understand and generate human language and can work multimodally—meaning it processes and generates text, code, and, depending on the version, images, audio, and video. It serves as a versatile AI assistant capable of answering complex queries, creating creative content, summarizing or translating texts, and supporting problem-solving.
Why is it useful for VET
Gemini supports Vocational Education and Training by personalizing learning processes, increasing the efficiency of trainers, and promoting the digital competencies of apprentices/trainees. It helps bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application:
- Personalized Support: Gemini can adapt learning content based on the trainee’s individual knowledge level and immediately answer specific questions about technical terms or work procedures [based on the benefits of AI in VET: 2061, 2062].
- Creation of Authentic Content: Trainers can use it to create realistic case studies, scenarios for simulations, or quiz questions tailored to specific vocational trades (e.g., for automotive mechatronics technicians, nurses, or industrial clerks).
- Problem Solving and Error Analysis: Trainees can input complex problems from their daily work and ask Gemini for structured step-by-step instructions for troubleshooting (e.g., for a machine error message).
- Research and Documentation Skills: Trainees can learn to formulate precise search queries (prompts) to quickly research and document relevant information on new technologies, legal changes, or industry standards [based on the benefits of Perplexity AI: 2332, 2337].
- Linguistic Support: It can translate technical terms and documents or rephrase complex issues into simpler language, thereby improving inclusion and access to learning materials.
How to
- Access: Gemini can be used across various platforms, including the official web interface, mobile apps (Android/iOS), or as an integrated function within Google Workspace (e.g., Google Docs).
- Account: A Google Account is required to save histories and use advanced features.
- Interaction: Users enter their requests (prompts) in natural language into the chat window and refine the results through follow-up questions to get a more precise answer.
Usage
|
Status |
Description |
|
✅ Free |
Free version with access to the base LLM. |
|
💠 Advanced |
Advanced features, including access to more powerful models (like Gemini Advanced), may be available via a Google One subscription or specific corporate accounts. |
|
🔑 Account required |
A Google Account is required for use. |
|
🌐 Cross-platform access |
Available via browsers and mobile apps. |
Learning Example
Scenario: A trainee in Heating, Sanitary, and Air Conditioning (HSAC) is tasked with explaining to a customer the advantages and the expected payback period of a new heat pump compared to a gas condensing boiler.
Process:
- The trainee asks Gemini: “Create an easy-to-understand overview summarizing the advantages and disadvantages of a heat pump in the HSAC trade and include a checklist for the initial consultation.”
- Gemini provides a structured answer, including technical details, energy efficiency factors, and a list of questions for the customer (e.g., insulation standard of the house, existing radiators).
- The trainee can follow up: “Can you explain the formula for calculating the Seasonal Performance Factor (SPF/JAZ) for the heat pump and include a fictitious example with values?”
- The trainee uses the generated and verified overview to prepare for the customer consultation, thus gaining practice-oriented feedback and directly applicable knowledge.
|
Title |
Content Focus |
Link |
|
Gemini Advanced Masterclass: From Beginner to Pro in 30min! |
Comprehensive tutorial covering the interface, extensions (including Google Flights and YouTube integration), and practical use cases for productivity. |
|
|
Introducing Gemini |
Our most capable AI model yet** |
A short introduction by Google DeepMind explaining the the model. |
|
Master 85% of Google Gemini in 12 Minutes (2025) |
Focuses on practical tips and use cases that last, including integration with Gmail and Google Sheets (relevant for the VET context of streamlining administrative work). |
|
|
Introduction to Gemini APIs and AI Studio |
More technical. Explains the developer tools, but gives insight into features like Code Execution and Function Calling, which show the powerful potential of the AI. |
6.6 🆕 Grok (AI model by AI for vocational education) #
What it is
Grok is an advanced AI language model developed by xAI, a company founded by Elon Musk. The latest version, Grok 4, features real-time search, integrated tool access, and adaptive text processing. Unlike many AI systems that rely solely on static training data, Grok can access current internet content and incorporate it directly into its responses.
Grok is available via the X platform (formerly Twitter) and is designed for users who want AI not just as a chatbot, but as a dynamic research and analysis tool.
Why it is useful for VET
Grok offers multiple benefits for vocational education:
🔍 Real-time research: Grok retrieves up-to-date information, ideal for fast-evolving fields like tech, law, health, or sustainability.
🧠 Technical text processing: Grok can summarize, explain, or rephrase complex content—perfect for learners in technical or business-oriented programs.
📊 Data extraction & analysis: Combined with tools, Grok can extract and structure data from texts—for example, for project reports or market studies.
📝 Report writing & documentation: Grok assists in drafting reports, protocols, or presentations—even in multiple languages.
🌐 Multilingual & integrable: Grok supports various languages and can be embedded into digital learning platforms.
How to use it
- Grok is accessible via the X platform (Twitter) – available through Premium+ or SuperGrok subscriptions.
- Grok 4 offers limited free access for testing.
- Requires an X account to sign in.
- Usable via web browser or mobile app.
- API access available for developers and institutions.
Learning Example
🛠 Scenario: A VET class in sustainability explores current trends in “Green Tech.”
Trainer:
- Assigns: “Research recent developments in sustainable energy and prepare a presentation.”
Learners:
- Use Grok to search for articles, studies, and market reports in real time.
- Summarize and simplify content with Grok’s help.
- Create a structured outline and generate visuals for their presentation.
- Discuss findings and reflect on the role of AI in learning.
🎯 Outcome:
Learners experience how AI helps them understand, organize, and creatively present complex information—a key skill in modern careers.
Usage
✅ Partially free (limited time)
💠 Full features via Premium subscription on X
🔐 Data privacy depends on platform policies
🌐 Accessible via web and mobile app
Links
Grok 4 vs. ChatGPT, Gemini & Copilot: The No-BS Comparison
Who Built Us & Why We Exist
|
Model |
Creator |
Core Mission |
|
Grok 4 |
xAI (Elon Musk) |
“Maximum truth-seeking, helpful, and a little sarcastic — like the Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy.” |
|
ChatGPT |
OpenAI |
“Safe, polished, mass-market friendly.” |
|
Gemini |
|
“Multimodal, integrated, infinitely scalable.” |
|
Copilot |
Microsoft + OpenAI |
“Productivity booster, glued into Office.” |
IF
|
You Want… |
Pick… |
|
Raw honesty + humor |
Grok 4 |
|
Safe, family-friendly AI |
ChatGPT |
|
Google integration + visuals |
Gemini |
|
Excel, Word, PowerPoint magic |
Copilot |
6.7 🆕 GrammarlyGO #
Link: https://www.grammarly.com/grammarlygo
Chapter context: Chapter 2 (Teaching & Learning), Chapter 3.1 (Writing tools)
What it is
GrammarlyGO is an AI-based writing assistant that helps with grammar, tone, and clarity. It can rewrite or improve entire texts.
Why is it useful for VET
Ideal for trainees writing reports, applications, or internship reflections. Also helpful for teachers reviewing learner writing.
How to
Use it in the browser or as an add-on to Word, Google Docs, or email. Sign-up is required. Free and Premium versions are available.
Learning Example
A hospitality student writes a motivational letter for an Erasmus+ internship and uses GrammarlyGO to refine grammar, structure, and wording.
Usage
✅ Free with account
💠 Premium version offers deeper analysis (monthly/annual plans)
Links
– https://www.grammarly.com/grammarlygo
8
6.8 🆕 JEDA.AI (Digital Board Tool) #
What it is
Collaborative dashboards, charts, images and more with JEDA.AI… Jeda AI is an artificial intelligence tool with which you can collaboratively create mind maps, AI images, flow diagrams, mind maps and more.
Why is it useful for VET
Supports Visual and Interactive Learning (Students can easily understand complex professional processes (e.g., electrical circuits, motor structures, sewing patterns, business flows, etc.) through diagrams, flowcharts, or visual maps. Jeda.ai’s whiteboard feature instantly visualizes a topic as the teacher explains it—thus making abstract knowledge tangible.)
Provides a Suitable Environment for Project-Based Learning (Students can work in groups on the same project on Jeda.ai (e.g., occupational safety plans, product design, cost calculations). They can easily create project ideas, draft reports, or presentations with AI-powered suggestions.)
Develops Digital Competencies (Digital literacy is one of the 21st-century skills in vocational education. Using Jeda.ai helps students think, produce, and plan with artificial intelligence tools.)
Save Time for Instructors (Teachers can quickly create lesson plans, educational content, or assessment tools on Jeda.ai. For example: “Occupational Safety in Welding” course (With AI, you can create a risk analysis table or safety poster for your company in minutes.)
Facilitates Interdisciplinary Work (Vocational training often requires collaboration between different fields (e.g., accounting + marketing, design + production). Jeda.ai facilitates collaboration between departments by providing a shared workspace.)
How to
JedaAI is free to use. It only requires a simple membership. Once you’ve approved the membership, you can start creating content immediately.
Usage
🆓 Free for everybody. 🔑 Account required (individual).
Learning Example
Learning by doing: The student creates their own digital board and draws the production process.
Collaborative learning: Group members work on the same Jeda.ai board.
Problem-based learning: Solutions are sought by asking AI questions like, “Why is productivity low in this production process?”
Meaningful learning: New tasks are compared with old projects using AI.
Links
Source 10.10.2025 https://www.jeda.ai/ai-whiteboard-for-education
6.9 🆕 Perplexity AI #
Link: https://www.perplexity.ai/
Chapter context: Useful in Chapter 2 (Teaching & Learning), Chapter 3.1 (Communication), Chapter 5.8 (Information & Research Tools)
What it is
Perplexity is an AI-powered search and research assistant that combines large language models with live web search to deliver accurate, cited answers. Unlike standard chatbots, Perplexity automatically includes sources for every answer, allowing users to verify information directly.
Its interface resembles a conversational search engine where users can ask questions, refine queries, and explore related topics in threads.
Key features include:
-
- Real-time web search integration for up-to-date information.
-
- Citations and source transparency, ensuring credibility.
-
- Follow-up questions for deeper exploration of a topic.
-
- File and image uploads for contextual Q&A (Pro version).
-
- Co-pilot mode for guided, step-by-step research.
-
- Collections to save and organize queries or results.
-
- Access to advanced AI models such as GPT-4, Claude 3, or Perplexity’s proprietary models in the Pro plan.
Why it is useful for VET
In vocational education and training (VET), Perplexity acts as a reliable, AI-assisted research companion. It supports:
-
- Quick access to industry-relevant, verified information (e.g., new regulations, materials, tools, or procedures).
-
- Efficient project preparation by summarizing large volumes of information.
-
- Evidence-based learning by providing cited sources and encouraging source evaluation.
-
- Digital literacy and critical thinking, as learners can cross-check AI-generated summaries with real references.
-
- Trainers and educators who need to prepare updated teaching materials, lesson content, or assessment tasks.
For VET institutions emphasizing self-directed and work-based learning, Perplexity helps trainees develop modern research and documentation skills—important for lifelong learning and employability.
How to
-
- Go to Perplexity.ai or download the mobile app.
-
- Start typing a question or topic (no login required).
-
- Review the generated summary, explore cited sources, and click on them for full articles.
-
- Use Follow-up questions to refine or expand your topic.
-
- Sign up for a free account to save searches and build Collections.
-
- Upgrade to Perplexity Pro for advanced model options (e.g., GPT-4, Claude 3), file uploads, and longer search threads.
Learning Example
A group of mechatronics trainees are developing a project on renewable energy systems in industrial settings. Using Perplexity, they:
-
- Search for “applications of solar automation in manufacturing plants.”
-
- Receive a summarized overview with cited sources from research papers and recent trade publications.
-
- Save key results in a Collection for their group report.
-
- Ask follow-up questions about “cost-efficiency” and “recent innovations,” refining their understanding before presenting their findings.
Their trainer uses the same tool to verify sources and prepare discussion questions for class.
- Ask follow-up questions about “cost-efficiency” and “recent innovations,” refining their understanding before presenting their findings.
Usage
✅ Free version available (no login required, limited features)
💠 Pro plan (monthly/annual subscription) for advanced AI models and enhanced tools
🔑 Optional account for saving searches and Collections
🌐 Web and mobile access (Android/iOS apps available)
Links
6.10 🆕 VIDU.AI (AI Video Generator) #
What it is
Vidu AI is an AI video generation tool — it can turn text, images, or ideas into videos automatically.
You can describe a scene (for example, “a veterinary student learning how to clean a wound on a dog”) and Vidu AI creates a realistic instructional video in seconds.
This makes it valuable for education and skills training, where showing “how something is done” is more effective than reading about it.
Why is it useful for VET
Vocational education focuses on practical, real-life skills — such as veterinary work, engineering, health services, mechanics, tourism, and more.
Vidu AI helps in several ways:
Visual Learning and Demonstration:Students can see the correct techniques visually — e.g., how to weld, how to take a blood sample, how to bake, or how to assemble a part. Teachers can generate realistic demo videos without filming expensive setups.
Personalized Training Content:Instructors can type custom instructions (“show a mechanic fixing a brake system in a workshop”) and Vidu AI instantly generates a tailored video.This allows creating localized, language-specific, and profession-specific content easily.
Cost & Time Efficiency:Traditional video production takes cameras, locations, actors, editing — very expensive. Vidu AI reduces that to a few text prompts, saving schools and teachers significant time and money.
Simulated Practice Environments :Students can observe or even interact with AI-generated training videos that simulate workplace environments. Useful for dangerous or hard-to-access jobs (e.g., construction, chemical labs, surgery, animal operations).
Accessibility & Inclusion :AI videos can include subtitles, voiceovers, or translations — helping students with disabilities or different language backgrounds.
How to
Vidu AI is free to use. It only requires a simple membership. Once you’ve approved the membership, you can start creating content immediately.
Usage
🆓 Free for everybody.
🔑 Account required (individual).
Learning Example
Veterinary Medicine: Animal care, injection techniques, and laboratory practice videos
Electrical-Electronics: Circuit setup, safety practice visualizations
Healthcare: Patient care, sterilization, and first aid simulations
Cooking: Training videos that visually explain recipe steps
Tourism and Hospitality: Customer communication, service techniques, and reception processes.
Links
More Features based on price:
6.11 🆕 Nano Banana (AI creative content generator) #
What is it?
Nano Banana is an online AI tool that helps you create short videos, animations, images, and music using simple text prompts. It turns your ideas into creative digital content in just a few seconds.
Why is it useful for VET
In VET, Nano Banana can be used to create engaging visual or audio materials for lessons, presentations, or social media. It helps students and teachers express ideas creatively, experiment with multimedia formats, and understand how AI supports digital creation.
How to
Go to the Nano Banana website, type a short description of what you want to create, and choose a format such as image, video, or sound. The AI will automatically generate the content, which can be downloaded or shared online.
Usage
🆓 Free basic access (limited generations).
💻 Works in browser, no installation needed.
🔑 Account required for saving or sharing creations.
Learning Example
VET learners use Nano Banana to design short AI-generated videos explaining safety procedures at the workshop. The tool helps them combine creativity with digital skills.
Links
• https://nanobanana.ai
• https://nanobanana.io (alternative access)
6.12 🆕 Deepseek (AI supporting VET) #
What it is
DeepSeek AI is a Chinese-based artificial intelligence company (Hangzhou DeepSeek Artificial Intelligence Basic Technology Research Co., Ltd.), founded in July 2023 by Liang Wenfeng.
Their core offering is a set of large-language models (LLMs) and AI tools (such as “R1”, “V3.2-Exp”) which are claimed to match or approach the performance of leading Western models at a significantly lower cost.
The company promotes “open-weight” model releases (i.e., model weights or configurations available under open licenses) and emphasis on cost-efficiency.
In practice, DeepSeek AI offers:
-
A chatbot/app/web interface for general-purpose querying and text generation.
-
Models specialized for code generation and reasoning tasks (for example, “DeepSeek-Coder” series) with large context windows and programming language support.
-
APIs and self-hosting possibilities (given open-weight availability) for organizations or developers.
Why it is useful for VET
Here are some of the ways DeepSeek AI could support VET environments—for learners, trainers, and programme designers:
-
Learners can use it to:
-
Ask technical or subject-specific questions (e.g., in IT, electronics, coding) and get model-generated explanations or help.
-
Experiment with a model that supports code generation or reasoning, useful for vocational programmes in software engineering, computer science, industrial automation, etc.
-
Explore multilingual or international content if the model supports multiple languages (which DeepSeek claims).
-
-
Trainers and curriculum designers can leverage it to:
-
Develop learning materials, generate exercises or prompts for students, or tailor tasks based on model output.
-
Provide students with a “sandbox” AI assistant to test prompts, ask for feedback, or simulate technical dialogue without always needing instructor input.
-
-
Institutional or project-based use: Because DeepSeek’s architecture emphasises cost-efficiency and open weights, educational institutes may consider deployment or integration (subject to licensing) for internal training labs, student projects, research tasks.
-
Communication and collaboration: The tool can support collaborative assignment workflows by generating draft content, summarising text, or acting as a peer-assistant for communication tasks.
In short: Like other advanced AI tools (e.g., ChatGPT), DeepSeek AI represents a next-generation digital tool that can shift how learners engage with technical content and how trainers design activities.
How to
Here’s a practical “How to” guide tailored for VET settings:
-
Visit the website (see link above) and check registration requirements.
-
Choose the appropriate version or model interface (web app, mobile app, or API).
-
There is an official web interface for “V3.2-Exp” and app access.
-
-
For students/training use:
-
Log in (or create an account if needed).
-
Use the chat interface: type your question or prompt, such as “Explain the difference between a transistor and a thyristor” (for electronics) or “Generate a Python script to automate network configuration”.
-
Review the response, ask follow-up questions, refine prompts.
-
-
For trainers/designers:
-
Use the model to draft exercise templates. Example: “Create 5 practical tasks for learners to configure a Linux server, with step-by-step instructions and checkpoints.”
-
Ask the model to critique learner responses or generate feedback.
-
-
If you are technically inclined or have institutional support:
-
Look into the API or model self-hosting options (since DeepSeek offers open-weight models). This enables deeper integration with your VET platform or custom training tools.
-
Ensure proper licensing, data governance, and security compliance if you self-host or integrate.
-
-
Important: Because DeepSeek is relatively new and has some regulatory or security concerns (see next section), ensure the tool is vetted for your educational context (data privacy, country usage, institutional policy).
Learning Example
Imagine a VET learner in an IT support course needs to set up a remote desktop service in Windows and check firewall rules. They could ask:
“How do I configure Windows Server 2022 to allow Remote Desktop connections, including firewall rule creation, user permissions, and network security best-practices?”
DeepSeek AI would generate a structured answer with step-by-step guidance. The learner could then follow, ask for clarifications (“What if I use Azure Virtual Desktop instead?”), or request a summary version. The trainer might ask the model to then produce a short quiz on the same topic: “Generate 3 multiple-choice questions about configuring Remote Desktop security in Windows Server.”
This demonstrates how the tool can be integrated into both learning (student asks) and teaching (trainer designs exercises) workflows.
Usage
✅ Free/low-cost access (depending on version) — good for individual learners or small-scale use.
💠 More advanced features (API, self-hosting, enterprise deployment) may require licensing, infrastructure and governance review.
News of partner countries #
The GPS4VET project emphasizes the importance of sharing experiences and innovations across partner countries. Each national context provides unique insights into how vocational education and training (VET) systems are adapting to digital transformation, integrating Web 2.x and AI tools, and preparing learners for future labour market challenges. The following sections present highlights from Ukraine, Germany, Poland, Türkiye, and Romania. They illustrate how different countries combine infrastructure investments, policy initiatives, and innovative learning platforms to strengthen VET in the digital age.
Germany #
Germany has been advancing digital transformation in vocational education and training (VET) through a combination of federal and regional initiatives. The Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) supports digital innovation in VET as part of the national strategy “Digital Education” and the program “DigiVET”. These initiatives emphasize the integration of digital tools, simulation technologies, and AI-based applications into curricula.
The DigitalPakt Schule, launched in 2019, has provided schools and vocational institutions with significant funding to improve their digital infrastructure. By 2025, more than €6.5 billion has been invested in broadband access, digital devices, and teacher training. In addition, the Alliance for Initial and Further Training focuses on strengthening digital competences of both learners and trainers.
Germany’s dual VET system, combining in-company training with part-time vocational schooling, benefits from platforms such as Metis (digital learning and collaboration tool for VET), ILIAS (open-source LMS with new AI features), and Vocational Training Online Campus (regionally hosted solutions). These platforms enable blended learning, digital portfolios, and workplace simulation.
Green skills and sustainability also play an important role in VET reform. Pilot projects, supported by chambers of commerce and industry (IHKs) and craft guilds (HWKs), integrate climate-friendly technologies and resource efficiency into training. AI literacy is increasingly promoted, ensuring that apprentices are prepared for both traditional and emerging job profiles.
In summary, Germany’s approach to digital VET is shaped by a strong infrastructure investment, a diverse platform landscape, and a close link between companies, schools, and policy-makers. This ensures that apprentices not only acquire technical competences but also develop transversal skills in digitalization, collaboration, and sustainability.
Poland #
Poland has accelerated the modernization of vocational education and training (VET) in recent years through reforms emphasizing employer cooperation, curriculum flexibility, and digital learning. The Ministry of National Education promotes digitalization within the Integrated Skills Strategy and through EU-funded projects. Strong broadband infrastructure supports the growing use of online platforms.
Digital tools such as Moodle, Google Workspace for Education, and national e-learning portals are widely adopted in schools and VET centres. Teachers increasingly integrate interactive materials, simulations, and online assessments into training. However, challenges remain in ensuring that all teachers and rural learners achieve a sufficient level of digital competence.
National and regional initiatives, such as FutureLab and Szkoła dla Innowatora (“School for Innovators”), aim to boost creativity, problem-solving, and entrepreneurship among students. Poland also places emphasis on connecting VET learners with the labour market, strengthening internships and dual-education elements.
Overall, Poland’s VET digitalization is advancing steadily, combining infrastructure investment with innovative teaching practices and closer industry links.
Ukraine #
According to the article of the Kyiv Global Government Technology Centre Team, nowadays, Ukraine is setting a precedent in GovTech-driven education and digital transformation with a focus on accessibility, lifelong learning, and alignment with global standards. Due to numerous training programs, online courses, and other educational initiatives, Ukrainians can access modern training programs in this area. As the GovTech Observatory of the Global Government Technology Centre in Kyiv informed, Ukraine has at least 22 educational GovTech initiatives today.
Since its establishment in 2019, the Ministry of Digital Transformation of Ukraine has set a goal to engage 6 million citizens in digital skills development programmes till 2024. The Digital Competence Framework for Citizens of Ukraine, aligning with European DigComp 2.1 methodology, was launched in 2021.
According to the sociological research on digital skills in Ukraine (conducted by the Ministry of Digital Transformation and the Eastern Europe Foundation within the EGAP program) in 2019, 53% of Ukrainians (aged 18 to 70) had digital skills below the basic level (according to the European Commission’s methodology); in 2021 – 47.8%; while in 2023 93% of Ukrainian adults had at least a minimum level of digital skills.
In January 2020, the national web platform for digital literacy and digital skills, «Diia.Digital Education» was launched. In less than 3 years, the goal of 6 million Ukrainians involved in digital literacy programs was achieved.
In May 2023, the national edutainment platform Diia.Education. was launched. This free and accessible platform provides educational series, simulations, tests to access digital or entrepreneurial skills and career guidance. Diia.Education promotes the concepts of «lifelong learning» as well as upskilling and reskilling. Some key features of the web platform:
-
- More than 370 free educational products. Educational series are produced without state funding and distributed via leading video platforms, such as «Megogo» and «1+1 video» to maximize accessibility. Additionally, prominent public figures (celebrities, influencers) are involved and the series have been broadcast by numerous regional TV channels.
-
- Digigram is a comprehensive digital literacy test based on European standards. About 1 mln (960,000) Ukrainians have already successfully assessed their skills and received certificates. There are also separate digital skills tests for teachers, civil servants, and healthcare professionals.
-
- The simulator module was launched in 2023. It presents video-driven scenarios that emulate workplace situations of the most popular occupations. This empower users to apply theoretical knowledge in practice, fostering adaptability and competence in diverse professional settings.
-
- A full-cycle personal development trajectory. It starts with an orientation test to identify strengths and interests, an Entregram test to assess entrepreneurial thinking or the Digigram and Cybergram tests to evaluate digital skills. Based on the results, users create their own personalized educational series, selecting from the available materials on the platform. Next, they can engage with an interactive simulator that replicates real-world professional or life scenarios. The final step is the profession tree and job catalog, featuring listings from the five largest national job search platforms, helping users explore career fields and submit resumes.
The project of the Ministry of Digital Transformation and the Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine on the Diia.Education platform — IT-Studios — are digital educational programs in computer science for students and teachers. The program covers digital literacy, media creativity, programming, and data analysis, which are taught through gamification and a project-based approach, problem solving etc. Since September 2023, every school has had access to IT studio materials.
CDTO Campus, a national educational initiative for preparing CDTOs (Chief Digital Transformation Officers) and their teams — digital leaders embedded within government bodies and local authorities responsible for leading and implementing digital transformation and innovative technological projects within public administration — plays an important role in the government’s digital education system. This app provides a convenient, accessible, and efficient educational experience — the so-called «University in a smartphone» — by delivering interactive tasks, simulations of real-world experience, and automated progress tracking.
The All-Ukrainian Online School is a web platform for 5-11 grade students and their teachers. It contains video lessons, tests, and materials for individual work in 18 core school subjects (more than 3,500 lessons) for blended and distance learning. The platform was developed by the Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine during the COVID-19 crisis, and is actively used after the russian invasion, as many Ukrainian students can’t attend their schools physically. For today, All-Ukrainian Online School has over 820,000 users from Ukraine and over 80 countries.
Moreover, the Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine has created a mobile application called «Can’t Wait to Learn» for students in 1-4 grades.
OsvitaNow is a free resource for teachers and parents, created in partnership with UNICEF Ukraine and the Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine. The platform is about children’s education, upbringing, and leisure during the war. It is updated weekly and is supplemented with materials on specific topics (e.g. forms of education, entering universities in Ukraine etc).
Mriia is the first educational state app for students, teachers, and parents. It is a fully autonomous integrated system for educational process and extracurricular activities. The app is currently in a pilot launch with 40 schools from six regions of Ukraine and the capital. However, in the nearest future it will be launched free of charge at all schools that wish to join. Mriia will have its own educational information system, connected to the state register of the Ministry of Education and Science.
Vocational education online is a digital learning platform that provides training courses for students of VET institutions and applicants for professional qualifications. During the full-scale invasion, enrollment in VET schools has been increasing. More than 13,000 people, including internally displaced people, veterans, and the unemployed, have been able to get a profession for free.
Among significant GovTech initiatives in education there are as well:
-
- NUMO – a web-based platform for children aged 3-6 developed by experts from UNICEF and the Ministry of Education and Science.
-
- Book`VAR – an educational digital platform for studying natural sciences using augmented and virtual reality, allowing visualizing physics experiments (for 8–11 grades).
-
- UNIVERA – a mobile application for students that provides an integrated class schedule, university news, a job search platform, and the ability to hold online elections. Since its launch, UNIVERA has more than 15,000 users.
-
- Ukraine.Inclusion – a portal for people with special needs, their parents, and professionals.
-
- Study in Ukraine – the Ukrainian government website for international students, managed by the Ukrainian State Center for International Education.
-
- STUDYPASS – an electronic document with student information necessary for travelling to Ukraine and studying.
-
- The Unified State Electronic Database on Education – an automated system for collecting, certifying, processing, storing and protecting data on providers and recipients of educational services in Ukraine. Its data from is used to produce state-issued documents on education, academic titles and degrees, licenses to provide educational services and accreditation certificates, and student cards.
-
- Applicant’s electronic cabinet – a system through which applications for admission to higher and vocational education institutions are submitted and accepted.
-
- Unified School – an information and communication automated system designed for educational institutions, students, their parents, and educational authorities. It provides unified electronic journals, diaries, online lessons, tests, etc.
-
- The Automated Information Complex of Educational Management – an electronic education management system for collecting, storing, managing, and using educational data.
-
- URIS National Electronic Research and Information System – an information system for collection, processing, storage of data on the results of professional scientific and technical activities of Ukrainian scientific institutions, higher education institutions and scientists.
-
- E-Journal – a free electronic journal and diary by the Institute of Educational Analytics for general secondary education institutions.
Türkyie #
Türkiye’s VET system, managed by the Ministry of National Education (MoNE), has undergone significant digital transformation since 2020. The nationwide platform EBA (Eğitim Bilişim Ağı) serves as the primary digital learning portal, offering millions of students access to interactive content, videos, and online exercises.
MoNE has introduced specialized VET digital toolkits, teacher training programs, and sector-specific learning platforms. AI and green economy topics are increasingly piloted in technical schools, reflecting national priorities in digital skills and sustainability.
In vocational schools, blended learning and digital simulations are becoming more common. Cooperation with industry ensures that curricula address the needs of sectors such as manufacturing, IT, and energy. The Vocational Education Development Program further supports modernization by introducing entrepreneurship and innovation modules.
Türkiye’s VET landscape highlights a balance between centralized digital infrastructure (via EBA) and sector-specific innovation projects, ensuring that learners are prepared for both local and global labor markets.
Romania #
Romania’s VET sector is undergoing a dynamic process of reform, supported by EU funding and national digitalization strategies. The Ministry of Education has prioritized investments in digital infrastructure, broadband access, and teacher training under the National Recovery and Resilience Plan.
Digital platforms such as Moodle, Microsoft Teams, and regional e-learning portals are increasingly used in vocational schools. Teacher training programs promote digital competence, and new curricula encourage entrepreneurship and blended learning approaches.
EU-funded initiatives, like EduCred and Digital Romania, support the development of innovative learning resources and inclusive access for rural and disadvantaged learners. Romania also emphasizes the integration of sustainability and green skills into vocational pathways, aligned with European policy frameworks.
Despite progress, challenges remain in reducing disparities between urban and rural areas and in ensuring equitable access to digital resources. Nonetheless, Romania’s VET modernization demonstrates a clear commitment to building a digitally skilled, future-oriented workforce.

Disclaimer / Copyright Notice
Parts of the material were created and structured with the assistance of ChatGPT (OpenAI, GPT-5). The content was generated to support analysis and reporting, and has been adapted and reviewed by the project team.
All trademarks and product names mentioned are acknowledged and remain the property of their respective owners.
29.8.25 Germany, Project team